Forex
The Ultimate Guide to Forex Trading for Beginners

The Ultimate Guide to Forex Trading for Beginners
Forex trading can seem intimidating and overwhelming to beginners, but with the right knowledge and tools, anyone can become a successful trader.
In this ultimate guide, we will provide a comprehensive overview of forex trading for beginners, including the basics of the forex market, how to get started, tips for success, and common mistakes to avoid.
What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the buying and selling of currencies in order to make a profit. It is the largest and most liquid market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of $6.6 trillion.
Forex trading is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, and is accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
The Basics of Forex Trading
Forex trading for beginners: Before diving into the world of forex trading, it is important to understand the basics. Forex trading involves the exchange of one currency for another, with the aim of making a profit from the fluctuations in exchange rates.
Currency pairs are quoted in terms of their bid and ask price. The bid price is the price at which a trader can sell a currency, while the ask price is the price at which a trader can buy a currency. The difference between the bid and ask price is known as the spread.
Leverage is a powerful tool that allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. However, it also increases the risk of losses.
Traders should only use leverage with caution and always have a risk management strategy in place.
Getting Started with Forex Trading
To get started with forex trading, beginners need to choose a reliable and regulated broker, such as X or Y.
A broker is a company that acts as an intermediary between traders and the forex market. They provide access to trading platforms, educational resources, and customer support.
Once a broker has been selected, traders need to open a trading account and deposit funds. Most brokers offer a variety of account types to suit different trading styles and experience levels.
Beginners should start with a demo account to practice trading with virtual funds before moving on to a live account.
Tips for Success in Forex Trading
Successful forex trading requires a combination of knowledge, skill, and experience. Here are some tips to help beginners on their journey:
- Develop a trading strategy: A trading strategy is a set of rules that govern when to enter and exit trades. It should be based on a thorough analysis of the market and the trader’s risk tolerance.
- Manage risk: Risk management is the key to long-term success in forex trading. Traders should use stop-loss orders to limit their losses and never risk more than they can afford to lose.
- Keep up with the news: The forex market is influenced by a variety of factors, including economic data, political events, and central bank decisions. Traders should stay informed of these developments and adjust their trading strategy accordingly.
- Use technical analysis: Technical analysis is the study of historical price data to identify patterns and trends. Traders can use technical indicators to help them make trading decisions.
- Stay disciplined: Emotions can often lead to impulsive trading decisions. Traders should stick to their trading plan and avoid making impulsive trades based on fear or greed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Forex Trading
There are several common mistakes that beginners should avoid when trading forex. These include:
- Overtrading: Overtrading can lead to losses and burnout. Traders should only trade when there is a clear opportunity to make a profit.
- Not using a stop-loss: A stop-loss order is an essential risk management tool that helps limit losses. Traders should always use a stop-loss when trading.
- Trading without a plan: Trading without a plan is a recipe for disaster. Traders should have a well-defined trading strategy that includes entry and exit rules, risk management, and a plan for monitoring and adjusting trades.
- Ignoring fundamental analysis: Fundamental analysis is the study of economic and political events that can impact the forex market. Traders who ignore fundamental analysis may miss important market-moving events.
- Chasing losses: Chasing losses is a common mistake that can lead to a downward spiral of losses. Traders should accept losses as a normal part of trading and avoid trying to recoup losses with larger trades.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the minimum amount of money needed to start forex trading?
- The amount of money needed to start forex trading depends on the broker and account type. Some brokers offer accounts with a minimum deposit of $50, while others may require a minimum deposit of $1,000 or more.
- Can forex trading be done from a mobile device?
- Yes, most brokers offer mobile trading platforms that allow traders to access their accounts and trade on the go.
- What is a pip?
- A pip is the smallest unit of measurement in the forex market. It represents the fourth decimal place in currency pairs, except for pairs that include the Japanese yen, where it represents the second decimal place.
- What is a margin call?
- A margin call occurs when a trader’s account equity falls below the required margin level. The broker will then request additional funds or close out the trader’s positions to bring the account back into compliance with the margin requirements.
- How can I learn more about forex trading?
- There are many educational resources available for forex traders, including books, online courses, webinars, and trading forums. Traders can also learn by practicing with a demo account.
- What is the difference between a market order and a limit order?
- A market order is an order to buy or sell a currency pair at the current market price. A limit order is an order to buy or sell a currency pair at a specified price or better.
- What is the best time of day to trade forex?
- The best time of day to trade forex depends on the trader’s strategy and the currency pairs being traded. Some traders prefer to trade during the busiest hours of the day, while others may focus on specific currency pairs or trading sessions.
Conclusion
Forex trading can be a rewarding and lucrative endeavor for beginners, but it is important to approach it with caution and a solid understanding of the market.
By following the tips and avoiding common mistakes outlined in this ultimate guide, beginners can set themselves up for long-term success in forex trading.
Remember to always trade with discipline, manage risk, and stay informed of the latest market developments.
Fact Check
We strive to provide the latest valuable information for our readers with accuracy and fairness. If you would like to add to this post or advertise with us, don’t hesitate to contact us.
Remember to share this post!
If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us!

Artifiсiаl Intelligenсe
Metaverse Unveiled: Breaking Down the Virtual Frontier with Raw Power and Unraveling Truths

Metaverse Unveiled: Breaking Down the Virtual Frontier with Raw Power and Unraveling Truths
The Metaverse Decoded: Understanding the Basics
Unleashing the Power Within: Metaverse’s Impact on Industries
Navigating the Virtual Landscape: Tools and Platforms
Metaverse Realities: Debunking Myths and Misconceptions
The Human Touch: Social Dynamics in the Metaverse
Metaverse Security: Navigating the Digital Wild West
Metaverse and Economy: Redefining Transactions
Metaverse and Education: A Classroom Without Borders
Future Horizons: What Lies Ahead for the Metaverse?
As we wrap up our journey, let’s peer into the future. What innovations and developments can we expect in the ever-evolving landscape of the Metaverse? Join us in envisioning the possibilities that lie ahead.
Conclusion: Embracing the Metaverse Revolution
FAQs: Unlocking Further Insights
Is the Metaverse only for gamers?
No, the Metaverse spans various industries, offering diverse experiences beyond gaming.
How secure is the Metaverse?
Security challenges exist, but proper precautions can ensure a safe experience in the virtual realm.
Can anyone access the Metaverse?
Yes, with the right tools and platforms, the Metaverse is accessible to a broad audience.
Are virtual currencies reliable in the Metaverse?
Virtual currencies play a significant role, offering secure and efficient transactions within the digital landscape.
What role does education play in the Metaverse?
Education in the Metaverse goes beyond traditional boundaries, offering innovative and interactive learning experiences.
By delving into each aspect of the Metaverse, we aim to equip you with the knowledge and insights needed to navigate this dynamic digital frontier with confidence and curiosity. Embrace the Metaverse revolution—your journey starts now.
Artifiсiаl Intelligenсe
Blockchain: A Comprehensive Guide to Decoding the Revolutionary Technology

Forex
Business Development is Not Sales!

Are you confused about the difference between business development and sales? You are not alone. Many people use the words interchangeably, but there are actually important differences between the two. In this blog post, we will explore what exactly business development is and how it differs from sales. We will also look at the benefits of business development and why it is an essential part of your business. By the end of this post, you will have a better understanding of the importance of business development and how it can help grow your business.
Read More: Tom advisor and educator
What is Business Development?
When it comes to business development, there is a lot of terminologies that you may not be familiar with. So, in this blog post, we will take a look at the difference between business development and sales, as well as discuss the different activities that are involved in each role. We will also provide a list of skills and resources that are necessary for success in business development, as well as some tips on how to maximize potential and achieve success.
First of all, let’s define the terms: business development is the process of helping a company reach its objectives by developing new relationships and partnerships. These two roles can be seen as opposites – sales focus on closing deals with customers while business development helps companies build relationships with potential partners.
There are several key differences between these two roles. For example, sales representatives typically focus on selling one product or service at a time while business developers may be involved in multiple negotiations at once. Additionally, sales representatives usually work within an established hierarchy while business developers work outside of traditional hierarchies to develop new relationships. Finally, businesses engage in traditional selling activities such as cold calling or visiting potential clients while businesses develop more creative strategies such as social media marketing or content marketing (which we will discuss later).
The benefits of engaging in business development activities depend largely on the company’s goals. If your goal is to increase revenue or market share then engaging in business development activities is likely going to help you reach those objectives faster than if you were relying solely on sales efforts. Additionally, when done correctly, business development can help create positive customer relationships which can lead to repeat purchase behavior down the line!
So now that you know what business development is and what it involves, it’s time to learn some skills and resources necessary for success! Business developers need strong communication skills so they can build trust with their partners and clients; they also need excellent networking abilities so they can find new opportunities and connect with relevant people within their industry. Furthermore, effective business developers have knowledge about various channels (such as online marketing or PR) so they can use them effectively when building relationships with clients or partners. Finally, businesses should use tools like proposal writing software (like Proposal) when creating proposals for potential deals – this will make the process easier and more efficient for both parties involved!
Thank you for reading our blog post, “What Is Business Development?”. In this article, we discussed the difference between Business Development and Sales and discussed the key differences.
Also, Read More: Best Ways for Workers’ Potential to Unlock Knowledge
Exploring Business Development Strategies to Grow Your Business
No business is ever successful without sales, and sales are only as good as the relationships that are formed along the way. In this section, we’ll be exploring the different roles that sales and business development play in a business. We’ll also be identifying key strategies for expanding your business, managing customer relationships effectively, marketing your product or service effectively, and closing deals successfully. By understanding these concepts and applying them to your own situation, you can achieve success in your field.
When it comes to defining the differences between sales and business development, there are several important points to consider. Sales are all about generating leads and converting them into paying customers – it’s about building relationships with potential clients. Business development is all about nurturing those relationships and helping clients reach their goals – it’s about taking care of the small stuff so that big things can happen.
In order to identify new partnership opportunities or manage customer relationships effectively, you need to have a clear understanding of what each role entails. Sales professionals need to know how to identify leads and convert them into buyers; business developers need to be able to understand client needs and help clients reach their goals; marketers need to know how to create multimedia content that engages customers; negotiators must be skilled in creating win-win solutions.
Once you’ve identified which path you want to take with regard TO YOUR BUSINESS AND WHAT YOU WANT FROM IT (or if you’re feeling lost), it’s time to start finding ways TO GET THERE! There are many different digital tools available today that can help support growth (such as social media platforms), but nothing works better than effective lead-generation tactics backed by an actionable roadmap! Crafting an effective sales pitch is critical for success in any field – whether you’re trying to sell software or cars! And finally, understanding key metrics such as monthly active users (MAUs) or revenue growth is essential for measuring progress and optimizing efforts accordingly!
Building Relationships Vs. Selling Products
Business Development is essential for any startup or small business that wants to grow. It’s the process of building relationships with potential customers and turning those relationships into sales. While there are many similarities between sales and business development, there are also a few key differences that need to be taken into account.
Most importantly, business development is about understanding the customer’s wants and needs. When done correctly, this can lead to more successful sales transactions. Additionally, Building relationships is essential for finding new customers and retaining current ones – two key factors in growing your business. Finally, it’s important to understand what motivates people in order to develop strategies that work well with them. By following these tips, you can build a successful Business Development strategy that will help your company grow!
In addition to these tips, Entrepreneurs can benefit from collaboration and networking when doing Business Development. These two activities help entrepreneurs connect with potential investors or partners, which can lead to more success in securing funding or making deals. staying up to date with industry trends is also important when doing Business Development – by keeping up with the latest news and developments in your industry, you’re better prepared when meeting with potential customers or partners.
No matter what type of Business Development you’re involved in (short-term or long-term), designing a successful sales strategy around customer relationships is essential for success. By following these tips, you’ll be on your way to building lasting connections with your customers!
The Benefits of Business Development
Business development is essential to any organization’s success. It’s responsible for helping to identify and cultivate new markets, developing strategies for creating new relationships with customers, partners, and suppliers, and more. There are many benefits to developing a strong business development strategy, including the following:.
First and foremost, business development helps to understand customer needs and tailor products/services to meet those needs. By understanding your customer’s wants and needs, you can provide them with products that they will truly appreciate. This leads to increased customer loyalty and better market share overall.
Next up is developing an efficient process for identifying and cultivating new markets. By using data analysis techniques and market research, you can identify new opportunities that you may not have otherwise seen. This helps you stay ahead of the competition – something that is essential in today’s competitive environment.
Another key benefit of business development is establishing valuable connections in the industry. These connections can be used to support your business expansion in a number of ways – from providing access to valuable resources to helping with marketing campaigns or product launches. Plus, these connections tend to be long-lasting – making them a valuable asset as your organization grows bigger.
Last but not least is monitoring competition and researching alternatives – two essential tasks in any successful business strategy. By staying on top of changes in the industry (and making sure that you’re always armed with fresh ideas), you’re less likely to get caught off guard by challenges or unforeseen events. And if things do start going wrong? Having a well-planned backup plan will help keep your company afloat until things turn around again!
To Sum Things Up
We hope that this blog post has helped you understand the differences between business development and sales, as well as the importance of developing relationships with customers. Business development is an important part of any business, and by understanding how to effectively utilize it, you can increase your chances of success. Keeping up with industry trends and understanding what motivates customers can create a successful strategy that will help your company grow. Take action today to start building strong relationships with potential partners and customers – it will pay off in the long run!
-

 Education2 years ago
Education2 years agoCreating Engaging And Relevant Content As A Literacy Influencer
-

 Internet3 years ago
Internet3 years agoWhat Are the Differences Between WP Rocket, RocketCDN and Cloudflare
-

 How To..3 years ago
How To..3 years agoWhat Is Better Than Safety Deposit Box
-

 Mobile Phones3 years ago
Mobile Phones3 years agoKnow About the New Upcoming Mobile Phones
-
 SEO2 years ago
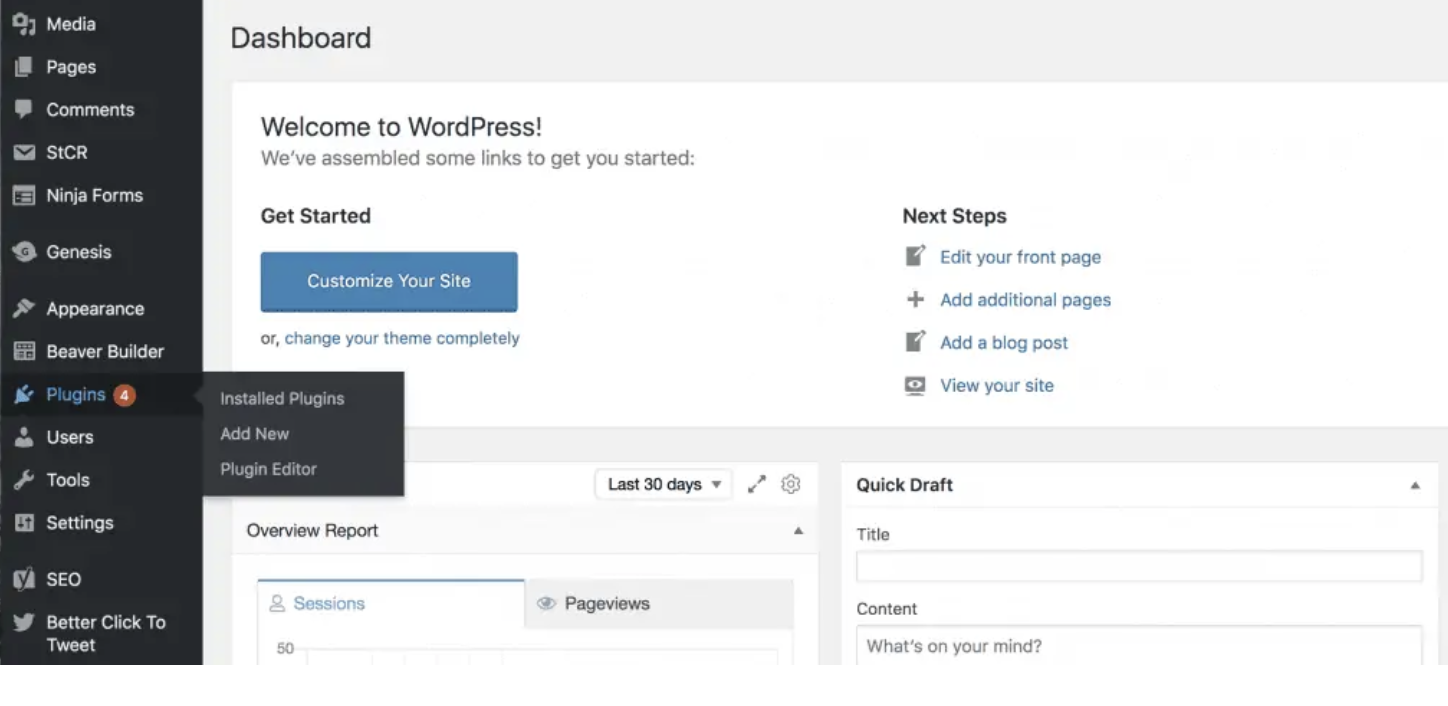
SEO2 years agoWordPress: How to Fix ‘Add New Plugin Menu Not Showing
-

 Digital Marketing1 year ago
Digital Marketing1 year ago13 Possible Reasons Why Your Google Ads Are Not Showing Up
-

 Software2 years ago
Software2 years agoWhy is Content Workflow Software Necessary for Content Production
-
TVs2 years ago
All You Need to Know About the Toman Tokyo Revengers