Cloud Tech
What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?

Natural language processing (NLP) is a field of Artificial Intelligence that focuses on the interactions between computers and human languages. NLP enables machines to understand, interpret and manipulate natural language in order to respond to user queries, generate insights from unstructured data and even create content. With the increasing use of voice assistants powered by NLP, more people are beginning to get familiar with this technology without even realizing it.
What is natural language processing?
Natural language processing (NLP) is an area of computer science and artificial intelligence that deals with how computers interact with humans in natural languages such as English, Spanish, and Chinese. Natural language processing enables computers to analyze large amounts of data in a more efficient way by understanding the context and meaning of words. This technology helps machines to understand the complexity of human language and process it accordingly.
The primary goal of NLP is to allow computers to interact with humans in natural conversations using speech recognition or text-based communication. It involves various processes such as identifying specific words in a sentence, analyzing relationships between them, interpreting user intent, translating from one language to another, summarizing documents, extracting information from unstructured text data, recognizing named entities such as people or places within a sentence and much more.Become a master of NLP by going through this NLP Training!
How does natural language processing work?
Natural language processing (NLP) is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on enabling computers to understand and process human language. Through the use of natural language processing, computers are able to interpret user input, recognize patterns in text, and generate meaningful insights from large amounts of data. By understanding the nuances of natural language and using sophisticated algorithms, NLP enables machines to answer questions posed by humans in a conversational manner.
At its core, natural language processing involves breaking down an input sentence into its individual components such as words and phrases and then analyzing these components for meaning. For example, an NLP system might take an input sentence like “I am looking for a restaurant” and recognize that it is asking for recommendations for restaurants.
NLP tools and approaches
Python and the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK)
Python is an increasingly popular programming language that has been used to develop a wide range of applications. One of the most powerful and versatile libraries for Python is the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK), which provides users with access to a comprehensive suite of natural language processing tools. NLTK enables developers to easily create programs that are capable of understanding written or spoken human languages in order to generate meaningful insights from text data.
The NLTK library contains many useful features such as tokenization, stemmers, taggers and parsers that allow developers to manipulate text data easily. It also includes modules for syntactic analysis, semantic analysis and discourse analysis as well as interfaces for interfacing with other natural language processing services like OpenNLP and Stanford CoreNLP.
Statistical NLP, machine learning, and deep learning
Statistical natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and deep learning are quickly becoming some of the most important tools in the world of artificial intelligence (AI). With their combined capabilities, these technologies have enabled the development of data-driven AI applications that can solve complex problems in a fraction of the time it would take a human.
Statistical NLP is a form of AI that uses algorithms to understand and interpret natural language. It enables computers to understand speech and text as they would be spoken by humans, allowing them to interact with us more naturally. Machine learning allows computers to learn from previous experience and data, making decisions based on what they have learned. Deep learning is an advanced form of machine learning that uses neural networks to mimic the way humans think and process information.
Why is natural language processing important?
Natural language processing (NLP) is an important field of computer science and artificial intelligence that enables computers to understand and interpret human languages. NLP has revolutionized the way we interact with machines, allowing us to give instructions in plain English instead of having to learn a specific coding language. This technology has been used in many different applications, such as search engines, virtual assistants, machine translation services, text analytics platforms, and more.
The evolution of natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) has been a topic of interest for computer scientists and linguists since the 1950s. It is a form of artificial intelligence that deals with the interactions between computers and human natural language in order to understand what humans mean when they communicate. Over the past few decades, NLP has evolved significantly to become more reliable and efficient, making it an invaluable tool for businesses, governments, healthcare organizations, and other institutions.
In recent years, the development of new algorithms such as deep learning have enabled machines to understand the complexity of language better than ever before. This has opened up a world of possibilities when it comes to using NLP for various tasks such as sentiment analysis or automated customer service. Additionally, advancements in cloud computing have resulted in increased access to massive datasets which can be used to train machine learning models that are more accurate than ever before.
Cloud Tech
Data Lakes on AWS: Building Scalable and Cost-Effective Data Lakes Using AWS Infrastructure

Organisations are constantly seeking efficient ways to store, manage, and analyse vast amounts of data. The data lake is a scalable and flexible solution for storing structured and unstructured data.
As cloud computing continues to evolve, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has positioned itself as a leader in facilitating the creation of data lakes, offering a suite of services that enable businesses to build scalable and cost-effective data storage solutions.
This blog explores how organisations can leverage AWS infrastructure to construct data lakes that not only streamline their data management processes but also unlock valuable insights.
For those looking to deepen their understanding or implement these solutions, AWS Training offers comprehensive resources and courses, particularly focusing on AWS Big Data services and best practices.
Understanding Data Lakes
The value of data lakes extends beyond mere storage; they enable comprehensive data analytics and machine learning capabilities by providing raw, unfiltered access to data.
This rawness is crucial for organisations aiming to gain a competitive edge through data-driven insights, as it allows for more flexible and detailed analysis than traditional data warehouses.
Data lakes facilitate a variety of analytics, from analyzing past data to real-time monitoring and predictions, catering to the diverse analytical requirements of modern businesses.
Moreover, data lakes facilitate a democratisation of data within an organisation. By removing silos and consolidating data in a central repository, they ensure that data is accessible to data scientists, analysts, and business users alike.
This accessibility accelerates innovation and decision-making processes, as stakeholders can leverage the full spectrum of organisational data for comprehensive insights.
Why Build Your Data Lake on AWS?
AWS provides a robust and diverse ecosystem for creating data lakes, offering unmatched scalability, security, and cost-effectiveness. With AWS, businesses can easily collect, store, and analyse data at scale, without worrying about the underlying infrastructure’s capacity or maintenance.
AWS’s pay-as-you-go pricing model further enhances its appeal, as it allows organisations to scale their data storage and processing capabilities up or down based on their needs, ensuring cost efficiency.
By adopting a data lake architecture, businesses can not only scale their data storage and processing capabilities as their data grows but also enhance their agility in responding to market changes and opportunities.
The flexibility to store and analyse any type of data, structured or unstructured, opens up new avenues for innovation and optimisation, making data lakes an indispensable asset for any organisation.
Key Components of AWS Data Lakes
Amazon S3
At the heart of AWS data lakes lies Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), renowned for its durability, availability, and scalability. S3 serves as the ideal foundation for a data lake, offering secure storage for vast amounts of data.
Features like S3 Lifecycle policies and S3 Intelligent-Tiering complement its capabilities by optimising storage costs through automatic data movement to the most cost-effective access tier.
AWS Lake Formation
AWS Lake Formation makes it easier to establish and protect a data lake by streamlining the setup process and enhancing data security. There are no spelling, grammar, or punctuation errors in the original text.
It automates time-consuming tasks such as data collection, cleaning, and cataloging, making it easier for users to access and analyse data. Lake Formation also enforces security policies and provides a centralised, secure location for data access.
Amazon Glue
Amazon Glue is a managed ETL service that prepares and transforms data for analysis. It automatically discovers and catalogs metadata from AWS data stores, making it accessible for search and query. Glue seamlessly integrates with Amazon S3, Amazon Redshift, and any JDBC-compliant data store, facilitating a wide range of data integration tasks.
Amazon Redshift
For analytics workloads, Amazon Redshift provides a fast, scalable, and fully managed data warehouse service. It integrates smoothly with S3, enabling direct SQL querying across the data lake.
This allows businesses to run complex analytics and machine learning algorithms on large datasets without moving the data, thus reducing the time and cost associated with data analysis.
Analytics and Machine Learning Services
AWS offers a comprehensive suite of analytics and machine learning services, such as Amazon Athena for serverless querying, Amazon QuickSight for business intelligence, and Amazon SageMaker for building, training, and deploying machine learning models. These services empower organisations to derive actionable insights and make data-driven decisions.
Building a Scalable and Cost-Effective Data Lake on AWS
Creating a data lake on AWS involves several key steps, starting with defining your data governance and security policies. AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is crucial for securing your data lake with fine-grained access control.
Once the foundational security measures are in place, the next step is to set up your storage with Amazon S3, creating buckets to store your data. Utilising AWS Lake Formation, you can then automate the process of data ingestion, cataloging, and preparation for analysis.
Integrating Amazon Glue for ETL processes ensures that your data is ready for analysis, while Amazon Redshift and other AWS analytics services allow for powerful querying and insights generation. By leveraging these AWS components, organisations can build a scalable, secure, and cost-effective data lake that meets their specific needs.
Conclusion
The journey to creating a data lake on AWS is a strategic move towards harnessing the power of big data. With the right approach and utilisation of AWS services, businesses can achieve a scalable, secure, and cost-efficient data management solution.
AWS Training provides essential learning paths for those interested in mastering the art of building and managing AWS data lakes, ensuring that organisations can fully leverage the potential of AWS big data services.
By embarking on this journey, companies can unlock new levels of insights and innovation, driving their success in the digital age.
Cloud Tech
2024 Cybersecurity Outlook: Brace Yourself for These 5 Emerging Threats (and How to Beat Them!)

2024 Cybersecurity Outlook: Brace Yourself for These 5 Emerging Threats (and How to Beat Them!)
In the ever-evolving realm of digital technology, cybersecurity remains at the forefront of concern for individuals, businesses, and governments alike.
As we step into 2024, the cyber threat landscape has become more complex and sophisticated than ever before.
The convergence of various technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing, has opened new frontiers for cyber threats that are more formidable and harder to detect.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with an in-depth understanding of the top five emerging cybersecurity threats of 2024 and provide actionable strategies to safeguard against them.
The significance of cybersecurity in today’s digital age cannot be overstated.
With the digitalization of almost every aspect of our lives, the potential for cyber threats has exponentially increased. Personal data, financial information, and even national security are at constant risk of cyber attacks.
The year 2024 presents unique challenges in this dynamic cyber battleground. One of the key trends we are witnessing is the use of AI by cybercriminals. AI, once a tool predominantly used for defense, is now being employed to orchestrate attacks with alarming precision and scale.
This shift calls for a proactive and advanced cybersecurity approach, integrating AI-driven defense mechanisms to stay ahead of attackers.
Another pivotal aspect of the 2024 cybersecurity landscape is the vulnerability of IoT devices. The proliferation of connected devices has created numerous entry points for cybercriminals.
These devices, often with inadequate security measures, can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to broader networks.
The challenge here is to secure a rapidly expanding ecosystem of interconnected devices, which requires a combination of robust security protocols, regular firmware updates, and user education.
Deepfake technology is another emerging threat that poses significant risks.
The ability to create hyper-realistic fake audio and video content can lead to sophisticated phishing scams, misinformation campaigns, and personal identity theft.
As this technology becomes more accessible, the potential for its misuse in cybercrime is a grave concern.
Identifying and combating deepfake-based cyber attacks requires not only advanced detection technologies but also heightened awareness and verification protocols.
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency.
However, this shift to cloud environments has given rise to a new form of cyber threat – cloud jacking. Unauthorized access and exploitation of cloud services can lead to data breaches, service disruption, and loss of sensitive information.
Securing cloud environments is, therefore, a critical component of any cybersecurity strategy in 2024.
Lastly, the ubiquity of mobile devices makes them a prime target for cybercriminals.
The increase in mobile-based financial transactions, coupled with the use of personal devices for work (BYOD), has heightened the risks associated with mobile device security.
Cyber attacks targeting mobile devices, such as malware, phishing, and man-in-the-middle attacks, are becoming increasingly common and sophisticated.
The purpose of this guide is not just to alert you to the potential dangers but to empower you with knowledge and strategies to protect yourself and your organization from these emerging cyber threats.
As we delve deeper into each of these areas, remember that staying informed, vigilant, and proactive is your best defense in the digital world of 2024.
Let’s embark on this journey together, understanding the risks and learning how to navigate the treacherous waters of cybersecurity in this dynamic era.
1. The Rise of AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
Introduction to AI in Cybersecurity
In 2024, the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity has become a double-edged sword.
While AI technologies offer groundbreaking solutions in protecting against cyber threats, they have also become a powerful weapon in the arsenal of cybercriminals.
The sophistication and efficiency of AI-powered cyber attacks have escalated, presenting unique challenges for cybersecurity professionals.
Understanding AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
AI-powered cyber attacks are a breed of sophisticated cyber threats that leverage machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence to carry out attacks.
These attacks are characterized by their adaptability, speed, and ability to learn from and evade detection systems.
Unlike traditional cyber attacks that follow a predefined approach, AI-powered attacks continually evolve, making them particularly challenging to detect and mitigate.
Types of AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
AI-Driven Phishing Attacks: These attacks use AI to personalize phishing messages by analyzing data from social media and other sources. This results in highly convincing phishing attempts that are more likely to deceive users.
Automated Malware Creation: AI algorithms can now generate new malware variants, automatically tweaking codes to bypass security systems and create zero-day threats.
AI-Powered Network Attacks: These involve AI systems learning network traffic patterns and mimicking them to infiltrate networks undetected.
Deepfake Technology in Cybercrime: AI-generated audio and video deepfakes are used in social engineering attacks, impersonating trusted individuals to gain sensitive information.
Challenges Posed by AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
The primary challenge in countering AI-powered cyber attacks is their evolving nature.
Traditional security systems that rely on known threat signatures are ineffective against AI threats that can alter their characteristics.
Additionally, AI attacks can analyze the response patterns of security systems and adapt to avoid detection, making them incredibly elusive.
Strategies to Combat AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
To effectively combat AI-powered cyber threats, organizations need to adopt a multi-faceted approach:
Advanced AI-Driven Defense Systems: Implement AI-based security systems capable of detecting and responding to threats in real time. These systems must be designed to learn and adapt to evolving threats continually.
Enhanced Detection and Response Capabilities: Use behavioral analytics and anomaly detection techniques to identify unusual patterns that might indicate an AI-powered attack.
Employee Training and Awareness: Regular training sessions for employees are crucial. They should be made aware of sophisticated phishing techniques and how to identify and respond to them.
Collaboration and Information Sharing: Collaborating with other organizations and sharing information about emerging threats can provide a broader understanding of AI-powered attacks and how to defend against them.
Regular System Audits and Updates: Conducting regular audits of cybersecurity systems and ensuring all software is up-to-date are critical practices in defending against AI-powered threats.
Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing: Employ ethical hackers to test the resilience of systems against AI-powered threats. Regular penetration testing can identify vulnerabilities before cybercriminals exploit them.
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
As we move further into 2024 and beyond, the role of AI in cybersecurity will continue to evolve.
On the one hand, AI provides advanced tools for protecting against cyber threats.
On the other, it presents a continually evolving threat as cybercriminals harness its power for malicious purposes.
The key to staying ahead in this cat-and-mouse game lies in continually evolving our cybersecurity strategies, investing in cutting-edge technology, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness.
In conclusion, while AI-powered cyber attacks pose a significant threat, with the right strategies and tools, organizations can protect themselves against these sophisticated attacks.
The future of cybersecurity is a constant race against emerging threats, and staying informed and proactive is the best defense.
2. The Exploitation of IoT Vulnerabilities
The Growing IoT Landscape
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the way we interact with technology.
In 2024, it’s estimated that there are tens of billions of IoT devices in use, from smart home devices to industrial sensors.
This proliferation of connected devices has significantly enhanced efficiency and convenience in both personal and professional realms.
However, this rapid expansion also presents a considerable challenge in cybersecurity, particularly with the exploitation of IoT vulnerabilities.
Understanding IoT Vulnerabilities
IoT devices are often designed with convenience and functionality in mind, sometimes at the expense of security.
Many devices lack robust security features, making them susceptible to hacking.
Common vulnerabilities include weak passwords, unsecured network services, lack of regular software updates, and insecure ecosystem interfaces.
Types of IoT Vulnerabilities and Exploits
Insecure Network Services: Many IoT devices are connected to networks with insufficient security protocols, making them easy targets for cyber attacks.
Weak Authentication/Authorization: Devices with default or weak passwords can be easily compromised, allowing unauthorized access.
Insecure Software/Firmware: Outdated software or firmware can contain known vulnerabilities that hackers exploit.
Insecure Ecosystem Interfaces: The interfaces between IoT devices and other components of their ecosystem (like cloud services or mobile apps) often have security gaps.
Real-World Consequences of IoT Security Breaches
The implications of compromised IoT devices are far-reaching.
For instance, a hacked smart home device can lead to unauthorized home access or personal data leakage.
In a business context, a breach in industrial IoT can lead to significant operational disruptions, financial loss, and safety hazards.
Moreover, compromised IoT devices can be used in larger network attacks, like DDoS attacks, leveraging the collective power of thousands of devices.
Strategies for Securing IoT Devices
Securing IoT devices requires a comprehensive approach that involves manufacturers, users, and regulatory bodies:
Secure Device Design and Development: Manufacturers must prioritize security in the design and development phase, incorporating robust encryption and secure software practices.
Regular Software/Firmware Updates: Regular updates are crucial for patching vulnerabilities. Automatic updates should be a standard feature for IoT devices.
Strong Authentication Protocols: Implementing strong password policies and multi-factor authentication can significantly enhance IoT security.
Network Segmentation and Monitoring: IoT devices should be isolated on separate network segments, and continuous monitoring should be employed to detect suspicious activities.
User Education and Awareness: Users must be educated about the importance of security practices, such as changing default passwords and securing their home networks.
Compliance with Security Standards and Regulations: Adhering to established IoT security standards and regulations can help ensure a baseline level of security across devices.
Challenges in IoT Security
One of the primary challenges in IoT security is the diversity and quantity of devices.
With a vast range of manufacturers and varying levels of security sophistication, establishing universal security standards is complex.
Additionally, many IoT devices have limited processing power and storage, making the implementation of advanced security measures challenging.
The Future of IoT Security
Looking ahead, the security of IoT devices will remain a critical concern.
As technology evolves, so do the capabilities of cybercriminals.
The future of IoT security lies in the development of more intelligent, adaptive security solutions capable of foreseeing and mitigating emerging threats.
This includes the integration of AI and machine learning for predictive threat analysis and the development of more secure, resilient IoT frameworks.
In conclusion, the exploitation of IoT vulnerabilities is a significant threat in 2024. However, with concerted efforts in secure device design, regular updates, user education, and adherence to security standards, we can mitigate these risks.
As IoT continues to grow and integrate into all aspects of life, prioritizing its security is not just a necessity but a responsibility we all share.
3. Deepfake Technology in Phishing Scams
The Evolution of Deepfake Technology
As we venture deeper into 2024, deepfake technology has rapidly evolved from a novel concept to a powerful tool used in cybercrime, especially in phishing scams.
Deepfakes, which are hyper-realistic digital forgeries of video or audio, have become increasingly sophisticated due to advancements in AI and machine learning.
This technological progression has made it extremely challenging to distinguish between real and forged content, making deepfakes a potent weapon in the arsenal of cybercriminals.
Understanding Deepfake Phishing Scams
Deepfake phishing scams involve the use of AI-generated audio or video clips to impersonate trusted individuals.
These scams are particularly insidious as they exploit the trust and authority of the impersonated individuals to deceive victims into divulging sensitive information, transferring funds, or granting access to secure systems.
Types of Deepfake Phishing Scams
CEO Fraud: Cybercriminals use deepfake audio or video to impersonate a company’s CEO or other high-ranking official to instruct employees to transfer funds or disclose confidential information.
Impersonation of Public Figures: Deepfakes of politicians, celebrities, or influencers are used to spread misinformation or manipulate public opinion.
Social Engineering Attacks: Deepfakes are used in sophisticated social engineering campaigns to gain the trust of individuals or to blackmail them.
The Impact of Deepfake Scams
The consequences of deepfake phishing scams are far-reaching.
They can lead to significant financial losses, damage to personal and corporate reputations, and erosion of public trust in media and communications.
In a business context, a successful deepfake scam can result in the exposure of sensitive corporate data, financial theft, and legal liabilities.
Challenges in Combating Deepfake Scams
One of the primary challenges in combating deepfake scams is the difficulty in detecting them.
As AI algorithms become more advanced, deepfakes become increasingly realistic and harder to identify with the naked eye.
Furthermore, the proliferation of deepfake-generating software has made this technology more accessible to cybercriminals.
Strategies for Mitigating the Risk of Deepfake Scams
To mitigate the risks posed by deepfake scams, a multifaceted approach is essential:
Advanced Detection Technologies: Investing in technology that can detect the subtle anomalies in deepfake videos or audio is crucial. This includes AI-powered detection tools that analyze inconsistencies in digital files.
Educating and Training Employees: Awareness training for employees is vital. They should be trained to recognize the potential signs of deepfake scams and verify the authenticity of suspicious communications.
Implementing Verification Protocols: Organizations should establish strict verification protocols for financial transactions or sensitive information sharing. This might include multi-person approval processes or secondary confirmation through a different communication medium.
Policy Development and Enforcement: Developing and enforcing policies that govern how sensitive requests are handled can reduce the risk of falling victim to deepfake scams.
Staying Informed About Deepfake Trends: Keeping abreast of the latest developments in deepfake technology and cybercrime tactics is essential for proactive defense.
The Ethical and Legal Implications of Deepfakes
Beyond the immediate threat to cybersecurity, deepfakes raise significant ethical and legal questions.
They challenge our notions of truth and authenticity in digital media.
The legal framework around deepfakes is still evolving, with governments and international bodies grappling with how to regulate this technology without impinging on freedom of expression.
The Future of Deepfakes and Cybersecurity
As we look to the future, the intersection of deepfakes and cybersecurity will continue to be a critical area of concern.
The ongoing arms race between deepfake creators and detectors will likely intensify, with both sides leveraging advancements in AI and machine learning.
Organizations must remain vigilant, continuously updating their defense strategies to counteract the evolving threat posed by deepfake technology.
In conclusion, deepfake technology in phishing scams presents a formidable challenge in 2024.
However, by employing advanced detection technologies, educating employees, implementing strict verification protocols, and staying informed about the latest trends, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to these sophisticated attacks.
The fight against deepfake scams is not only a technical challenge but also a test of our collective resilience and adaptability in the face of emerging cyber threats.
4. Cloud Jacking: The New Frontier in Cyber Threats
Introduction to Cloud Jacking
As we navigate through 2024, the widespread adoption of cloud computing has brought forth a new cyber threat: cloud jacking.
This term refers to unauthorized access and manipulation of cloud computing environments.
With businesses increasingly relying on cloud services for data storage, processing, and hosting, the implications of cloud jacking are significant and far-reaching.
Understanding Cloud Jacking
Cloud jacking exploits vulnerabilities in cloud computing systems.
This can range from compromised credentials and hijacked accounts to exploiting weaknesses in cloud infrastructure and services.
Unlike traditional cyber-attacks that target specific corporate networks, cloud jacking can have a cascading effect, affecting multiple clients hosted on the same cloud service.
Forms of Cloud Jacking
Account Hijacking: Through phishing attacks or credential theft, attackers gain access to cloud service accounts, enabling them to manipulate data and services.
Exploitation of Configuration Weaknesses: Misconfigured cloud settings are a common entry point for attackers, often leading to data breaches.
API Vulnerabilities: Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that are used to manage and interact with cloud services.
Insider Threats: Disgruntled employees or those with malicious intent can misuse their access to cloud environments.
Impact of Cloud Jacking
The impact of cloud jacking is extensive.
It can lead to data theft, loss of data integrity, service disruption, and a significant breach of client trust. For businesses, this can translate into financial loss, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage.
Challenges in Preventing Cloud Jacking
Preventing cloud jacking is challenging due to the complex nature of cloud environments.
The shared responsibility model of cloud computing, where security is divided between the cloud provider and the client, often leads to ambiguity in security roles.
Additionally, the dynamic and scalable nature of the cloud makes monitoring and managing security more complex.
Strategies to Counter Cloud Jacking
To combat cloud jacking, a comprehensive approach is needed:
Strong Authentication and Access Controls: Implement robust access control measures, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) and least privilege access, to minimize unauthorized access.
Regular Security Audits and Compliance Checks: Conduct frequent audits of cloud environments to ensure compliance with security policies and standards.
Secure API Management: Ensure that APIs are securely designed and regularly monitored for unusual activities.
Employee Training and Awareness: Educate staff about the risks of cloud jacking and best practices for securing cloud environments.
Incident Response Planning: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan specifically tailored to address cloud security incidents.
Encryption and Data Protection: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest in the cloud, ensuring that data remains secure even if unauthorized access occurs.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection: Use advanced monitoring tools to continuously scan for suspicious activities within cloud environments.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of Cloud Security
As cloud computing becomes more prevalent, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on cloud security.
Compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is crucial.
Businesses must ensure they are compliant with relevant data protection and privacy laws, which include requirements for securing cloud environments.
The Evolving Threat Landscape in Cloud Computing
The threat landscape in cloud computing is constantly evolving.
As cloud service providers introduce new features and technologies, new vulnerabilities may emerge.
Cybercriminals are continuously developing new methods to exploit these vulnerabilities, making it imperative for businesses to stay abreast of the latest security trends and threats in cloud computing.
The Future of Cloud Security
Looking ahead, cloud security will remain a critical area of focus.
The adoption of emerging technologies like AI and machine learning in cloud security will play a key role in enhancing threat detection and response.
Additionally, there will be an increased emphasis on developing more sophisticated and integrated security solutions that can provide comprehensive protection across various cloud services and platforms.
In conclusion, cloud jacking presents a significant challenge in the realm of cybersecurity in 2024.
To effectively counter this threat, businesses must adopt a multi-layered security approach, focusing on robust access controls, continuous monitoring, compliance, and employee education.
As the cloud environment continues to evolve, staying vigilant and proactive in cloud security practices will be essential in safeguarding against the ever-evolving threat of cloud jacking.
5. Mobile Device Vulnerabilities: A Rising Cybersecurity Threat
The Proliferation of Mobile Devices
In 2024, mobile devices have become ubiquitous, integral to both personal and professional spheres of life.
With the vast majority of people owning smartphones and the increasing popularity of tablets and wearable technology, the mobile landscape presents a fertile ground for cybercriminals.
These devices, often containing a wealth of personal and corporate data, are attractive targets for a variety of cyber attacks.
Understanding Mobile Device Vulnerabilities
Mobile device vulnerabilities stem from a variety of sources, including outdated operating systems, insecure apps, unsecured Wi-Fi connections, and physical theft or loss of the devices.
These vulnerabilities can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information, eavesdrop on communications, or even use the devices as entry points to broader corporate networks.
Types of Threats Targeting Mobile Devices
Malware and Ransomware: Malicious software designed to infect mobile devices, steal data, or lock the device until a ransom is paid.
Phishing Attacks: Deceptive messages designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Attackers intercept communication between the mobile device and a network, often on unsecured Wi-Fi networks.
Cryptojacking: Unauthorized use of a mobile device’s resources to mine cryptocurrency.
Spyware: Software that secretly monitors and collects user information.
The Impact of Mobile Device Security Breaches
The consequences of mobile device security breaches are significant.
For individuals, it can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and privacy invasion.
For businesses, a compromised mobile device can result in data breaches, intellectual property theft, compliance violations, and damage to reputation.
Challenges in Mobile Device Security
Securing mobile devices is challenging due to their portable nature and the diversity of operating systems and applications.
Users often prioritize convenience over security, neglecting to update their devices or using insecure networks.
Additionally, the bring-your-own-device (BYOD) trend in workplaces adds another layer of complexity, as personal devices used for work purposes create a blend of personal and corporate data, complicating the security landscape.
Strategies for Enhancing Mobile Device Security
To protect against mobile device vulnerabilities, a comprehensive strategy is required:
Regular Software Updates: Keeping the device’s operating system and applications updated is crucial for protecting against known vulnerabilities.
Use of Security Applications: Installing reputable security software can help detect and prevent malware and other threats.
Secure Wi-Fi Practices: Avoid using public or unsecured Wi-Fi networks for sensitive transactions, and use a virtual private network (VPN) for added security.
Phishing Awareness and Training: Educate users on recognizing phishing attempts and the importance of not clicking on suspicious links or downloading attachments from unknown sources.
Implementation of BYOD Policies: Establish clear policies for employees who use personal devices for work, including requirements for security software and regular device audits.
Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data stored on mobile devices to protect it in case of loss or theft.
Physical Security Measures: Use lock screens, biometric authentication, and remote wipe capabilities to protect devices if they fall into the wrong hands.
The Role of Manufacturers and Developers
Mobile device manufacturers and app developers play a critical role in maintaining device security.
They must ensure that devices and apps are designed with security in mind, regularly release security patches, and respond promptly to identified vulnerabilities.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
With the growing reliance on mobile devices, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on mobile security.
Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, extends to mobile devices, requiring businesses to ensure that personal data accessed or stored on these devices is adequately protected.
The Future of Mobile Device Security
Looking ahead, the security of mobile devices will continue to be a major concern.
The advancement of technology will bring new types of devices and applications, each with its unique security challenges.
Future security measures may include more advanced biometric authentication methods, AI-based security monitoring, and the integration of security at the hardware level of mobile devices.
Conclusion
As we stand at the threshold of 2024, the cyber threat landscape has never been more dynamic or challenging.
The rise of AI-powered cyber attacks, exploitation of IoT vulnerabilities, sophisticated deepfake phishing scams, the emerging threat of cloud jacking, and the increasing vulnerabilities in mobile devices all represent significant challenges for individuals and organizations alike.
These evolving threats highlight the critical need for a proactive, informed, and multi-layered approach to cybersecurity.
In response to these challenges, it is imperative that we not only leverage advanced technology solutions but also foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness and education.
The integration of AI in defense strategies, the securing of IoT ecosystems, the development of detection technologies for deepfakes, the fortification of cloud environments, and the reinforcement of mobile security practices are essential steps in this ongoing battle.
Furthermore, the role of collaboration and information sharing cannot be overstated. In a landscape where threats evolve rapidly, staying informed and adapting to new challenges is crucial.
This requires not only vigilance but also a willingness to learn and innovate continuously.
In conclusion, the cybersecurity outlook for 2024 is a reminder of the relentless nature of cyber threats and the importance of staying ahead of them.
By understanding these threats and implementing robust strategies, we can safeguard our digital assets and maintain trust in the technology that plays such a pivotal role in our daily lives.
As we navigate through these challenges, let us remember that cybersecurity is a shared responsibility, and our collective efforts are the key to a safer digital future.
FAQs
How important is individual user awareness in combating cyber threats?
Individual user awareness is crucial. Many cyber attacks exploit user ignorance or negligence. Educating users on recognizing and responding to threats can significantly reduce the risk of successful attacks.
Can small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) afford advanced cybersecurity solutions?
Yes, many cybersecurity solutions are scalable and can be tailored to the needs and budgets of SMEs. Additionally, basic security practices like regular software updates, strong passwords, and employee training can be highly effective and cost-efficient.
Are there any emerging technologies that promise to revolutionize cybersecurity in the near future?
Technologies like quantum computing and blockchain hold great potential in revolutionizing cybersecurity. Quantum computing could enhance encryption methods, while blockchain offers improved security for transactions and data integrity.
How frequently should an organization conduct cybersecurity audits?
The frequency of cybersecurity audits depends on the organization’s size, data sensitivity, and the rapidly changing cyber threat landscape. Ideally, conducting audits annually or bi-annually, along with continuous monitoring, is recommended.
Is it safe to use public Wi-Fi in 2024?
Using public Wi-Fi still poses risks, especially if the network is unsecured. Using a VPN can help secure your connection, but it’s best to avoid accessing sensitive information over public Wi-Fi networks.
Valid Reference Links
- Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) – Emerging Threats: https://www.cisa.gov/emerging-threats
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) – IoT Security: https://www.nist.gov/iot
- Deepfake Detection – Tools and Techniques: https://www.deepfakedetection.com
- Cloud Security Alliance – Best Practices: https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/research/best-practices
- Mobile Security Best Practices – 2024: https://www.mobilesecurity2024.com
Artifiсiаl Intelligenсe
5G Unleashed: Redefining Connection, Weaving Futures

5G Unleashed: Revolutionizing Connectivity and Communication
Imagine a world where data flows like lightning, where connections are instantaneous, and possibilities bloom like wildflowers after a spring rain.
This, my friends, is the world 5G Unleashed has unveiled. In a digital era where connectivity is our oxygen, 5G isn’t just a faster internet; it’s a revolutionary leap, a turbo boost propelling us into an age of unimaginable speed, unwavering reliability, and limitless innovation.
“5G Unleashed” isn’t just a catchy tagline; it’s a battle cry, a declaration of transformative power.
This isn’t a gradual evolution; it’s a paradigm shift, a complete reshaping of how we connect, communicate, and experience the digital landscape.
Picture downloading movies in mere seconds, not agonizing minutes. Imagine virtual reality worlds so crisp and responsive, they feel real. Envision smart cities where devices whisper to each other, orchestrating a symphony of efficiency and convenience.
But 5G Unleashed isn’t just about speed thrills; it’s about unlocking possibilities that were once science fiction.
Imagine remote surgery performed by robots miles away, guided by surgeons in real-time.
Think of immersive education where virtual classrooms transport students to the heart of history or the depths of the ocean.
Picture autonomous vehicles gliding through seamlessly connected cities, transforming our commutes into effortless journeys.
The unleashing of 5G isn’t just happening in the future; it’s pulsating in the present. It’s in the hands of doctors performing groundbreaking surgeries, the eyes of students exploring virtual galaxies, the minds of engineers weaving the fabric of tomorrow’s smart cities. 5G Unleashed is a revolution unfolding, a tidal wave of progress reshaping our lives, one click, one connection, one innovation at a time.
So, embrace the unleashing. Let the speed wash over you, the reliability ground you, and the innovation inspire you.
This is the dawn of a new era, a digital renaissance powered by the unleashing of 5G.
The Rise of 5G: A Quantum Leap in Connectivity
The journey of 5G technology begins with a quantum leap in connectivity. Unlike its predecessor, 4G, 5G operates at speeds that were once deemed unimaginable.
With download speeds reaching up to 20 gigabits per second, the era of buffering and lag is becoming a distant memory.
Seamless Integration with IoT: A Symbiotic Relationship
One of the most significant aspects of 5G is its seamless integration with the Internet of Things (IoT).
Imagine a world where your devices communicate with each other in real-time, making decisions and adjustments on the fly.
This symbiotic relationship between 5G and IoT is ushering in an era of unparalleled convenience and efficiency.
Empowering Smart Cities: Beyond the Horizon
As 5G becomes more widespread, the concept of smart cities is no longer confined to the realm of science fiction.
The low latency and high capacity of 5G networks are empowering municipalities to implement innovative solutions for traffic management, energy consumption, and public safety.
The 5G Ecosystem: A Thriving Hub of Innovation
The 5G ecosystem is a thriving hub of innovation, fostering the development of groundbreaking technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR).
The enhanced network capabilities of 5G provide a fertile ground for developers to create immersive experiences that were once only conceivable in the realms of imagination.
Enhanced Mobile Broadband: Redefining Mobile Experiences
With 5G, mobile broadband is not just faster; it’s a complete redefinition of the mobile experience.
Streaming high-definition content, engaging in seamless video calls, and downloading large files on the go are now a reality, thanks to the remarkable speed and capacity of 5G networks.
The Human Touch: Impact on Daily Lives
Let’s take a moment to ponder the impact of 5G on our daily lives. From streaming our favorite shows without a hint of buffering to participating in lag-free video conferences, 5G is seamlessly woven into the fabric of our existence, enhancing our digital experiences in ways we could not have foreseen.
Navigating the Challenges: Security and Privacy Concerns
However, with great power comes great responsibility. The rapid evolution of 5G technology has raised concerns about security and privacy.
As we delve deeper into the era of 5G, addressing these challenges becomes paramount to ensure a secure and trustworthy digital environment.
The Road Ahead: Future Prospects of 5G
Looking ahead, the future prospects of 5G are nothing short of exhilarating. From enabling advanced autonomous vehicles to revolutionizing healthcare through remote surgeries, the possibilities seem boundless.
As we stand on the precipice of this technological revolution, the question arises: What else can 5G unleash upon the world?
Conclusion: Embracing the 5G Revolution
In conclusion, the 5G revolution is not merely a technological upgrade; it’s a paradigm shift that is reshaping the way we connect and communicate. As we embrace the full potential of 5G, we find ourselves on the cusp of a new era where the boundaries of innovation are pushed beyond what we thought possible.
FAQs: Unveiling the Mysteries of 5G
- Is 5G safe for human health? Yes, extensive research and studies have shown that 5G technology poses no significant risks to human health. Regulatory bodies ensure that the deployment of 5G adheres to strict safety standards.
- Q: How does 5G impact battery life on mobile devices? A: Contrary to common belief, 5G technology is designed to be energy-efficient. While initial implementations may have seen increased power consumption, ongoing advancements are addressing and mitigating these concerns.
- Q: Are there rural areas that still lack 5G coverage? A: Yes, the rollout of 5G is an ongoing process, and some rural areas may still be awaiting full coverage. Telecom companies and governments are actively working to expand coverage to ensure inclusivity.
- Q: Can 5G be a replacement for traditional home broadband? A: In some cases, yes. 5G’s high-speed and low-latency capabilities make it a viable alternative to traditional home broadband, providing reliable connectivity for various applications.
- Q: How does 5G contribute to environmental sustainability? A: 5G enables the implementation of smart systems that optimize energy consumption, contributing to environmental sustainability by reducing overall energy usage in various sectors.
Remember, as the 5G revolution unfolds, the possibilities are endless, and the impact on our lives will be profound. Embrace the future, as 5G continues to unleash a wave of innovation that will shape the digital landscape for years to come.
Verified Source References:
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- 5G Americas – Wireless Broadband Alliance
- IEEE Communications Society
- Ericsson Mobility Report
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
-

 Education2 years ago
Education2 years agoCreating Engaging And Relevant Content As A Literacy Influencer
-

 Internet3 years ago
Internet3 years agoWhat Are the Differences Between WP Rocket, RocketCDN and Cloudflare
-

 How To..3 years ago
How To..3 years agoWhat Is Better Than Safety Deposit Box
-

 Mobile Phones3 years ago
Mobile Phones3 years agoKnow About the New Upcoming Mobile Phones
-
 SEO2 years ago
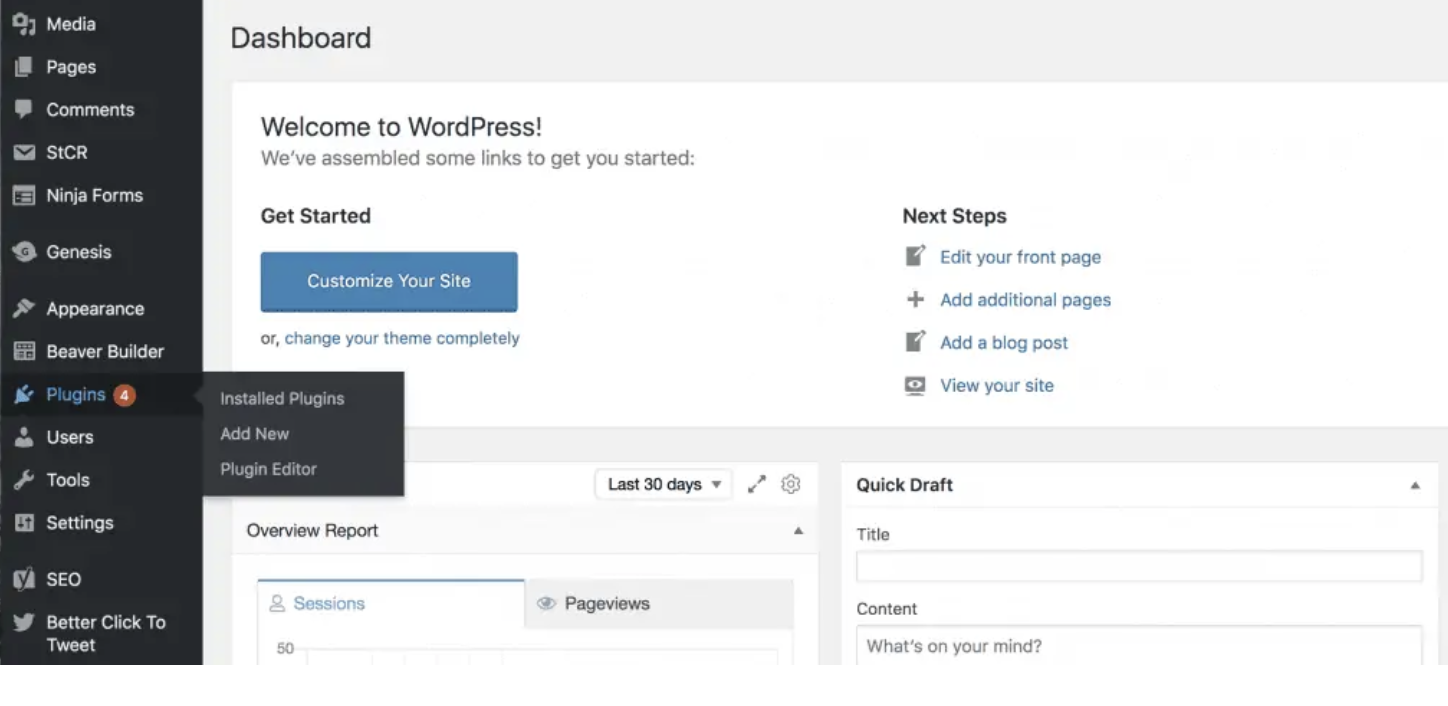
SEO2 years agoWordPress: How to Fix ‘Add New Plugin Menu Not Showing
-

 Software2 years ago
Software2 years agoWhy is Content Workflow Software Necessary for Content Production
-

 Digital Marketing1 year ago
Digital Marketing1 year ago13 Possible Reasons Why Your Google Ads Are Not Showing Up
-
TVs2 years ago
All You Need to Know About the Toman Tokyo Revengers