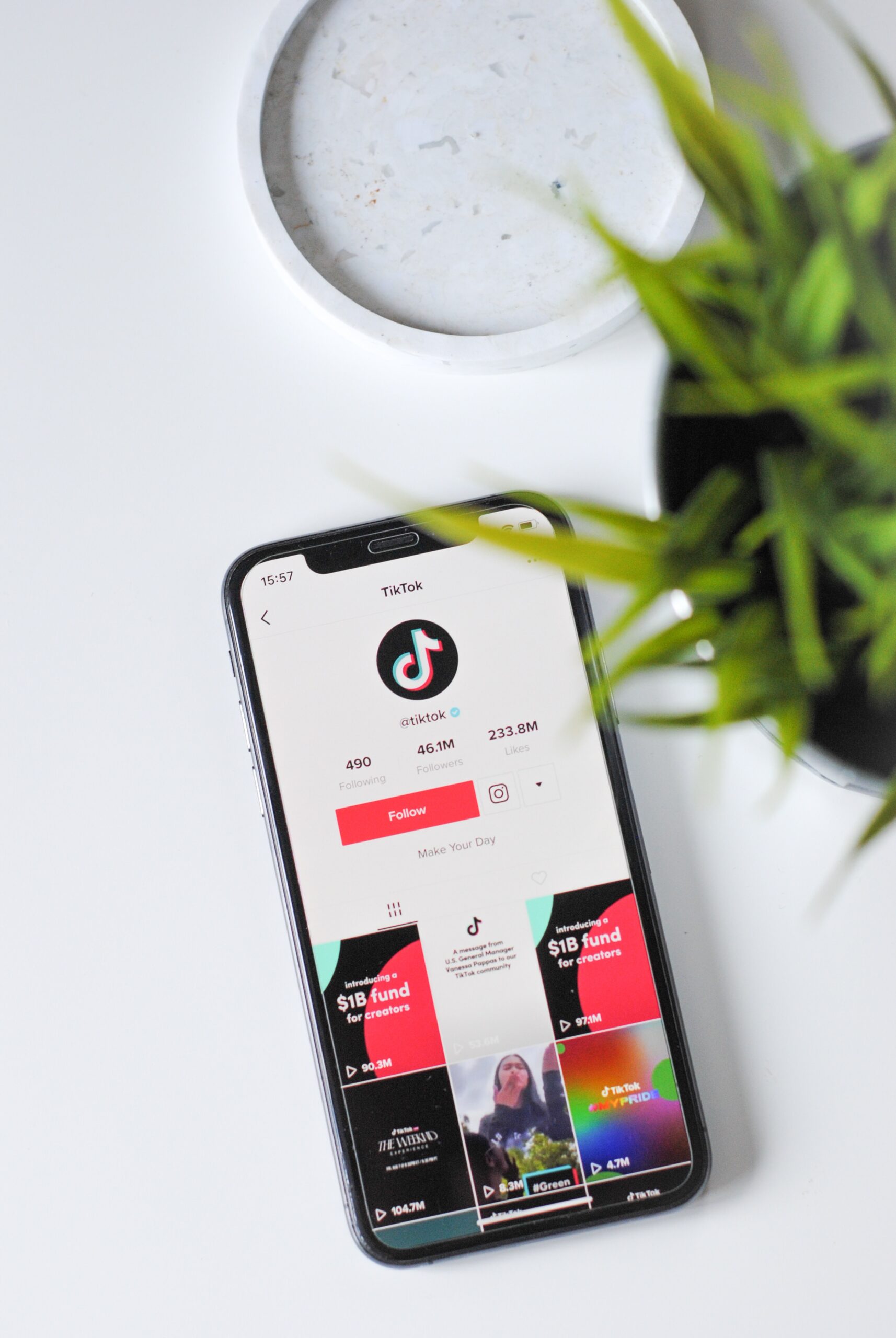
Tech News
EP3 Neopixel Lightsabers: Version Types and Features
The iconic lightsabers wielded by Anakin Skywalker and other Jedi in the Star Wars franchise have become a symbol of courage, strength, and hope for generations. Bring this classic weapon to life with EP3 Neopixel Lightsabers. These lightsabers feature innovative Neopixel technology that provides unparalleled visual effects when dueling or spinning in the dark. With several versions available on the market today, each offering unique features and benefits, there is sure to be an EP3 Neopixel lightsaber perfect for your dueling needs!
Obi-EP3 RGB Version Lightsaber Features
The Obi-EP3 lightsaber and Anakin skywalker Neopixel are advanced technology lightsabers designed for maximum performance during duels and spins. This lightweight yet durable option is made from metal alloy and has a comfortable handle for a firm grip. Some of its features are:
- It has ten sets of sound fonts
- 12 kinds of colors
- Volume adjustment
- Removable chassis
- Blaster, lock up, flash on clash
- Speaker and RGB Blade
- Advanced motion sensors
Various sound effects can be activated with the flick of a button to add drama to your dueling experience. The blade also has a shutter system, allowing users to switch between two colors in battle. In addition, the Obi-EP3 includes advanced motion sensors that detect the speed at which the lightsaber is moved, providing greater control and accuracy when striking or slashing.
EP3 Proffie V2.2 Version Lightsaber Features
The EP3 Proffie V2.2 lightsaber is a compelling Neopixel technology in lightsabers for dueling designed for experienced duelists who demand the best performance from their weapons. This sleek and lightweight model offers an impressive array of features, including:
- It has 22 sets of sound fonts
- Accept custom functions through 32g SD cards or cable
- Volume adjustment
- Changes color
- Removable chassis
- Volume adjustment
- Music
- Blaster lock up, flash on clash
- Speaker and Pixel Blade
- Built-in WS2812 light bar
A powerful processor allows users to customize their blade color, length, and power level. Advanced motion sensors detect even the slightest movement during battle, providing greater accuracy in strikes and slashes. Finally, users can also take advantage of the 3D model printing capability to create unique designs for their lightsaber blades!
SN Pixel and Ghv3 Version
These two versions have similar features:
It has 16 sets of sound fonts
22 sets of color or light effects
Built-in speaker
18650 battery with fast charging capability
Volume adjustment
Removable chassis and blades
Music
The SN Pixel utilizes advanced Neopixel technology to provide stunning visual effects during battle. The Ghv3 version has a flash-on-clash effect and enhanced motion sensors, allowing users to wield their saber more accurately in combat. Both versions offer powerful-yet-lightweight construction for a comfortable handle and maximum maneuverability.
No matter which version of EP3 Neopixel Lightsaber you choose, these models offer a variety of features and benefits that make them an ideal choice for any duelist. Whether you’re looking for a lightweight and durable version or a powerful and advanced option, EP3 Neopixel Lightsabers have something for everyone. Get ready to bring your Jedi adventures to life with one of these fantastic sabers today!
Artifiсiаl Intelligenсe
Beyond Passwords: Your Digital Self in the Age of Blockchain (Clickbait: Ditch Passwords Forever! This Tech Will Secure Your Online Life)

Beyond Passwords: Your Digital Self in the Age of Blockchain (Clickbait: Ditch Passwords Forever! This Tech Will Secure Your Online Life)
Tired of password Purgatory? Enter the Blockchain Oasis.
Remember that frantic morning scramble, brain aching for the elusive password to your bank account?
Or the sinking feeling when “incorrect password” flashes back, mocking your best guess?
We’ve all been there, prisoners of our own digital fortresses, locked out by the very keys meant to protect us. But what if we told you there’s a better way, a passwordless paradise called blockchain technology?
Think of it as your digital Swiss bank account, secure and impregnable.
Unlike the flimsy walls of traditional passwords, easily breached by hackers and cracked by brute force, blockchain builds fortresses with ironclad cryptography.
Your data, from medical records to online purchases, isn’t hoarded by corporations or vulnerable to centralized attacks.
Instead, it lives on a distributed ledger, a communal vault encrypted across thousands of computers, each one a guardian vigilantly watching over your digital self.
This isn’t just about convenience (though ditching those sticky notes is a major perk!). This is about ownership and control.
Blockchain empowers you to be the gatekeeper of your digital life. You decide what information you share, with whom, and for how long.
No more Big Brother data slurping or shady companies monetizing your privacy. You become the sovereign ruler of your own digital kingdom, wielding the keys to unlock or deny entry.
Imagine accessing your healthcare records without divulging them to every hospital you visit.
Picture transferring money across borders, instantly and securely, without banks taking a hefty cut.
Envision a world where your online identity isn’t a mosaic scattered across corporate servers, but a unified passport you carry with pride, granting access to services based on your own terms.
This is the promise of blockchain: a future where security isn’t a fragile wall of passwords, but a vibrant ecosystem of trust and empowerment.
Are you ready to leave Password Purgatory behind and step into the Blockchain Oasis? Buckle up, savvy internet user, because the revolution has just begun.
The Downside of Traditional Passwords
Why Are Passwords Failing Us?
In our digital age, passwords are the guardians of our online identities, yet they are failing us in more ways than one. Despite being the first line of defense in digital security, traditional passwords are increasingly becoming the weakest link. Let’s explore why.
The Illusion of Strength in Complexity
Think of the last time you created a password. Chances are, you were prompted to include a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols – the more complex, the better, right?
However, this complexity often leads to passwords that are hard to remember and, ironically, not as secure as we think. Cybersecurity experts have long debunked the myth that complexity equates to security.
In reality, it’s the length and unpredictability of passwords that matter most. But even then, no password is impervious to the sophisticated tactics employed by hackers today.
The Human Factor: Password Fatigue and Security Risks
As humans, we have our limits in remembering complex strings of characters. This leads to password fatigue – the tendency to reuse passwords across multiple accounts for convenience.
It’s like using the same key for your house, car, and office; if one gets lost or stolen, everything is compromised. This common practice significantly heightens the risk of mass data breaches.
Once a hacker cracks one password, they potentially gain access to an entire suite of an individual’s personal and professional digital life.
The Hacker’s Playground: Vulnerabilities in Password-Based Security
Hackers have a plethora of tools at their disposal to breach password-protected accounts. Techniques like brute force attacks, where automated software tries countless combinations until it finds the right one, are surprisingly effective against weak passwords.
Phishing attacks, where users are tricked into revealing their passwords, are increasingly sophisticated and difficult to spot.
Even when we think our passwords are safely stored, large-scale data breaches at major companies reveal that this is not always the case.
The Cost of Password Management and Recovery
The administrative burden of managing and recovering passwords is another often-overlooked downside.
For businesses, the cost of resetting passwords and dealing with security breaches can be astronomical.
For individuals, the time and effort spent managing passwords, coupled with the anxiety of keeping them safe, are a significant mental burden.
Biometric Authentication: A Step Forward but Not a Panacea
The advent of biometric authentication – using fingerprints, facial recognition, or retinal scans – seemed like a promising solution.
However, while biometrics offer convenience, they are not without their flaws. Biometric data, once compromised, cannot be changed like a password.
There are also privacy concerns and the potential for misuse of biometric data by corporations or governments.
Looking Beyond Passwords: The Need for a Paradigm Shift
The limitations of traditional passwords highlight the need for a paradigm shift in digital security.
We need a solution that is both secure and user-friendly, something that doesn’t require us to remember complex strings of characters or put our personal biometrics at risk.
This is where blockchain technology comes into play, offering a new way to authenticate identities and secure data without the pitfalls of traditional passwords.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while passwords have been the cornerstone of digital security for decades, their numerous shortcomings are increasingly apparent in our connected world.
As cyber threats evolve, so must our approach to securing our digital lives.
The future of digital security lies in innovative technologies like blockchain, which promise to offer a more secure, efficient, and user-centric approach to protecting our digital identities.
Blockchain: The Game-Changer in Digital Security
How Does Blockchain Enhance Security?
In the digital world, where data breaches and cyber threats loom large, blockchain emerges as a beacon of hope, promising a more secure and trustworthy online environment.
But what exactly makes blockchain a game-changer in digital security? Let’s unpack this.
The Immutable Ledger: A Foundation of Trust
At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger technology. Imagine a ledger that is not maintained by a single entity but is spread across a network of computers, each holding a copy of the ledger.
This decentralization is key to blockchain’s power. Once a record is added to the blockchain, altering it is next to impossible.
This immutability provides a foundation of trust and security unprecedented in digital transactions.
Decentralization: The Antidote to Centralized Risk
Centralization in traditional digital systems creates a single point of failure, a treasure trove for cybercriminals. Blockchain disrupts this by distributing data across a vast network, thereby diluting the risk.
Even if a part of the network is compromised, the rest remains unscathed, preserving the integrity of the entire system.
Cryptography: The Art of Secret Keeping
Blockchain employs advanced cryptography to secure the data.
Each block in the chain is secured with a cryptographic hash, a mathematical algorithm that turns data into a unique string of characters. Any change in the data alters the hash dramatically.
This means that tampering with a block would require altering all subsequent blocks, an almost Herculean task given the computational power required.
Transparency and Anonymity: A Balancing Act
Blockchain strikes a unique balance between transparency and anonymity.
While all transactions are visible to everyone in the network, the identities of the parties involved are protected.
This transparency ensures accountability and trust, while anonymity safeguards user privacy.
Smart Contracts: The Protocols of Trust
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, are a revolutionary aspect of blockchain.
They automate and enforce contractual obligations, reducing the need for intermediaries and the risk of fraud or manipulation.
Beyond Cryptocurrency: Diverse Applications of Blockchain in Security
Blockchain’s potential extends far beyond the realms of cryptocurrency.
In digital identity verification, it offers a secure way to manage and authenticate identities without centralized databases.
In supply chain management, it ensures the authenticity and traceability of products. In voting systems, it can provide secure and transparent electoral processes.
Challenges in Blockchain Adoption
Despite its potential, blockchain’s adoption faces hurdles.
Scalability, energy consumption, and the integration with existing systems are significant challenges. Furthermore, regulatory uncertainties and a lack of widespread understanding of the technology hinder its broader acceptance.
Preparing for a Blockchain-Enabled Future
As we stand on the brink of a blockchain revolution in digital security, it’s essential to educate ourselves about this technology.
Businesses and individuals alike must stay informed about the latest developments in blockchain and explore how it can be integrated into their digital practices.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology offers a new paradigm in digital security, promising a more secure, transparent, and efficient way to safeguard digital assets and identities.
As we move forward, embracing this technology and overcoming its challenges will be key to building a safer digital world.

The Mechanics of Blockchain Security
Understanding the Nuts and Bolts
Blockchain security is often hailed as a groundbreaking innovation, but how does it really work? What makes it so secure and reliable?
Let’s dive into the mechanics of blockchain security and understand what sets it apart.
The Anatomy of a Blockchain
Picture a blockchain as a series of digital ‘blocks’ linked together in a chain.
Each block contains a set of transactions or data, securely encrypted.
Every time a new block is added, it is verified by multiple nodes (computers) in the network, making fraud or alteration extremely difficult.
The Power of Decentralization
Decentralization is the heartbeat of blockchain security.
Unlike traditional systems where data is stored on central servers, blockchain distributes data across a network of nodes.
This means there’s no single point of failure, making it incredibly resistant to cyber-attacks and data breaches.
Cryptography: The Backbone of Blockchain Security
Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques. Each block contains a unique cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure link.
Altering any information would change the hash, alerting the network to the tampering. This cryptographic chaining ensures the integrity and chronological order of the blockchain.
Consensus Protocols: Ensuring Network Agreement
Blockchain operates on consensus protocols, rules that dictate how transactions are verified and added to the block.
Popular protocols like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) ensure that all nodes in the network agree on the state of the ledger, preventing fraudulent transactions.
Smart Contracts: Automating Trust
Smart contracts on the blockchain automatically execute transactions when predetermined conditions are met.
These contracts run on code and eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of manipulation and increasing efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its strengths, blockchain isn’t without challenges.
Issues like scalability, energy consumption (especially with PoW), and integrating blockchain into existing systems remain significant hurdles.
There’s also the concern of ‘51% attacks’ in some blockchains, where if more than half the network’s computing power is controlled by one entity, they could potentially manipulate the network.
Conclusion
Blockchain security offers a robust and innovative approach to protecting digital information.
Its combination of decentralization, cryptography, and consensus protocols provides a level of security far beyond traditional methods.
As the technology matures and overcomes its current limitations, blockchain stands to revolutionize how we secure our digital world.
Blockchain vs. Passwords: A Comparative Analysis
Why Blockchain Wins
In the digital security arena, blockchain and traditional passwords represent two very different philosophies.
While passwords have been the cornerstone of digital security for decades, blockchain introduces a paradigm shift.
Let’s compare these two to understand why blockchain is emerging as the superior option.
Traditional Passwords: The Aging Security Guard
Think of traditional passwords as an aging security guard. They’ve been around for a long time, are familiar, but they’re not as effective as they used to be.
Passwords are vulnerable to a range of attacks – from brute force to phishing – and they rely heavily on human memory and behavior, which can be fallible.
Blockchain: The Digital Fort Knox
On the other hand, blockchain can be likened to a digital Fort Knox. It doesn’t rely on single-key entry like passwords.
Instead, it offers a distributed, immutable ledger with complex cryptographic techniques.
This makes blockchain inherently more secure, as altering any part of the chain would require an astronomical amount of computing power.
User Experience: Complexity vs. Simplicity
One of the biggest drawbacks of passwords is their complexity and the user fatigue they cause. In contrast, blockchain can streamline the user experience.
With blockchain, users can potentially have a single digital identity for multiple platforms, eliminating the need to remember numerous passwords.
Decentralization: Eliminating Single Points of Failure
Passwords often involve centralized databases, creating single points of failure. Blockchain distributes data across a vast network, significantly reducing this risk.
Even if a part of the network is compromised, the rest remains secure, safeguarding the overall integrity.
Recovery and Revocation: A Clear Winner
Losing a password can lead to a cumbersome recovery process. Blockchain offers a more resilient approach.
For instance, with decentralized identity solutions, users can recover their identity through distributed mechanisms, without relying on a central authority.
Scalability and Adoption Challenges
Despite its advantages, blockchain faces its own set of challenges, particularly in scalability and widespread adoption.
Integrating blockchain into existing systems and ensuring it can handle large volumes of transactions are areas that need addressing.
Conclusion
Comparing blockchain with traditional passwords illustrates why blockchain is poised to be the future of digital security.
Its decentralized nature, enhanced security features, and user-friendly potential make it a formidable tool against cyber threats.
As blockchain technology overcomes its current challenges, it could render traditional passwords obsolete, ushering in a new era of digital security.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain in Security
Blockchain in Action
The realm of blockchain extends far beyond the confines of cryptocurrency.
Its unique attributes are being harnessed in various sectors, revolutionizing the way we think about and implement digital security.
Let’s explore some of the most impactful real-world applications of blockchain technology.
Revolutionizing Digital Identity Verification
One of the most significant applications of blockchain is in digital identity verification.
Traditional methods of identity verification are fraught with risks – from data breaches to identity theft.
Blockchain introduces a decentralized approach, where users can control their digital identities without relying on a central authority. This method not only enhances security but also offers greater privacy and control to individuals.
Transforming Supply Chain Management
In supply chain management, blockchain is a game-changer.
It provides a transparent and tamper-proof record of transactions and movements of goods.
This transparency ensures the authenticity of products, combats counterfeit goods, and enhances trust among consumers and businesses alike. From farm to table or manufacturer to retailer, every step is verifiable and secure.
Secure Voting Systems
Blockchain is making strides in securing electoral processes.
By leveraging blockchain, voting systems can become more secure, transparent, and resistant to tampering. This application could revolutionize democracy, making elections more accessible and trustworthy.
Healthcare Data Management
In healthcare, blockchain can securely manage patient records, ensuring privacy and data integrity.
It provides a secure platform for sharing medical records between authorized individuals and institutions, improving the efficiency and accuracy of diagnoses and treatments.
Challenges and Considerations
While these applications are promising, challenges such as scalability, regulatory compliance, and integration with existing systems remain.
There is also a need for a broader understanding and acceptance of blockchain technology among the general public and within specific industries.
Conclusion
The real-world applications of blockchain in security demonstrate its potential to revolutionize how we manage and protect digital information.
As the technology evolves and these challenges are addressed, blockchain is set to play a pivotal role in shaping a more secure and efficient digital world.
Overcoming the Challenges of Implementing Blockchain
Tackling the Obstacles
Blockchain technology, despite its potential, is not without its challenges.
Implementing blockchain in existing systems and processes requires navigating a complex landscape of technical, regulatory, and practical hurdles.
Let’s delve into these challenges and explore how they can be overcome.
Scalability: The Growing Pains of Blockchain
One of the primary challenges facing blockchain is scalability.
As the number of transactions on a blockchain increases, so does the need for greater computational power and storage.
This can lead to slower transaction times and higher costs, making it less practical for large-scale applications.
Solutions like sharding, where the blockchain is divided into smaller, more manageable pieces, and layer 2 solutions that process transactions off the main chain, are being explored to address this issue.
Energy Consumption: A Sustainable Dilemma
Blockchain, especially those using Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, can be energy-intensive.
This raises concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain technologies.
Transitioning to more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS) or exploring renewable energy sources for mining operations are ways to mitigate this issue.
Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the Legal Landscape
The decentralized and often borderless nature of blockchain poses significant regulatory challenges. Different countries have varying regulations regarding digital transactions, data privacy, and cryptocurrency.
Ensuring compliance while fostering innovation requires a delicate balance and ongoing dialogue between technology providers, users, and regulatory bodies.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating blockchain technology with existing digital infrastructures can be complex. Compatibility issues, the need for technical expertise, and the disruption of established processes can pose significant barriers.
Developing user-friendly blockchain solutions and providing education and training can facilitate smoother integration.
Security Concerns: Addressing Vulnerabilities
While blockchain is inherently secure, it is not immune to risks.
Potential security issues, such as 51% attacks, smart contract vulnerabilities, and key management challenges, need to be addressed.
Continuous research and development, alongside robust security protocols, are essential to bolster blockchain security.
Conclusion
Overcoming the challenges of implementing blockchain is crucial for realizing its full potential.
This involves addressing scalability and energy consumption issues, navigating regulatory landscapes, integrating with existing systems, and bolstering security measures.
As we tackle these obstacles, blockchain’s promise in transforming digital security becomes increasingly attainable.
The Future of Blockchain in Personal Security
What Lies Ahead
The horizon of personal security is being redrawn by blockchain technology.
As we edge further into the digital era, blockchain is poised to play a critical role in shaping our digital identities and safeguarding our online activities.
Let’s explore the promising future of blockchain in personal security.
Blockchain as a Guardian of Digital Identities
Imagine a world where your digital identity is as unique and unforgeable as your DNA.
Blockchain makes this possible. With its ability to create tamper-proof digital identities, blockchain is setting the stage for a future where identity theft and fraud become relics of the past.
These blockchain-based identities could replace traditional login credentials, offering a more secure and convenient way to access online services.
Enhanced Privacy and Control Over Personal Data
In an age where data breaches are commonplace, blockchain offers a beacon of hope. It empowers individuals with greater control over their personal data.
Instead of entrusting personal information to multiple organizations, blockchain allows individuals to store their data securely and share it selectively, using cryptographic keys.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and Personal Wealth Management
The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) is another area where blockchain is set to transform personal security. By removing intermediaries, DeFi platforms offer more control and security over personal financial transactions.
Blockchain’s transparency and security features make it an ideal backbone for these platforms, promising a more secure and equitable financial ecosystem.
Challenges and Opportunities in Personal Security
The journey towards a blockchain-powered future is not without challenges.
Issues like public acceptance, technological literacy, and regulatory frameworks need to be addressed.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and education in the realm of personal security.
Conclusion
As blockchain technology matures, its potential to redefine personal security is immense.
From securing digital identities to revolutionizing personal finance, blockchain stands as a pillar of trust and security in the digital world.
Embracing this technology could lead us to a future where our digital lives are more secure, private, and under our control.
How to Prepare for the Blockchain Revolution
Getting Ready for Change
The blockchain revolution is not just coming; it’s already here. But how do we prepare for this seismic shift in digital security?
Whether you’re an individual, a business leader, or a technology enthusiast, gearing up for the blockchain era requires a proactive approach. Here’s how to get ready.
Educating Yourself and Your Team
Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to emerging technologies. Start by educating yourself about blockchain technology.
Online courses, webinars, and industry conferences are great resources. If you’re leading a team or an organization, consider facilitating blockchain training sessions to stay ahead of the curve.
Evaluating Blockchain Applications in Your Life or Business
Look at how blockchain could apply to your personal life or your business operations.
This might involve exploring blockchain-based solutions for data storage, identity verification, or even investment opportunities in the blockchain space.
Participating in Blockchain Communities and Networks
Engagement with blockchain communities can provide invaluable insights and keep you updated on the latest trends and developments.
Online forums, social media groups, and local meetups can serve as platforms for discussion and networking.
Experimenting with Blockchain Technologies
Hands-on experience is one of the best ways to understand blockchain.
Consider experimenting with blockchain applications, such as using a blockchain-based service or investing in cryptocurrencies.
This practical exposure can demystify the technology and reveal its potential applications in your life.
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape
Stay informed about the regulatory environment surrounding blockchain technology, especially if you’re considering it for business applications.
Keeping abreast of legal and compliance issues is crucial to navigating the blockchain space successfully.
Conclusion
Preparing for the blockchain revolution involves education, experimentation, and engagement with the blockchain community.
By taking these steps, individuals and businesses can position themselves to harness the benefits of blockchain technology and navigate the challenges it presents.
The future belongs to those who are ready to embrace change and innovate, and blockchain is a field ripe with opportunities for both.
Debunking Myths about Blockchain Security
Separating Fact from Fiction
Blockchain technology, while revolutionary, is often shrouded in myths and misconceptions, especially regarding its security aspects.
It’s crucial to separate fact from fiction to understand the true capabilities and limitations of blockchain security. Let’s debunk some common myths.
Myth 1: Blockchain is Inherently Invulnerable
Fact: While blockchain’s design makes it highly secure, it’s not infallible. Issues like code vulnerabilities in smart contracts and potential 51% attacks on certain types of blockchains can pose risks.
However, compared to traditional databases, blockchain’s decentralized and cryptographic nature makes it significantly more secure against common cyber threats.
Myth 2: All Blockchains are Public and Transparent
Fact: Not all blockchains are created equal.
While public blockchains offer transparency and decentralization, private blockchains control access more strictly, offering privacy and efficiency.
The choice between public and private blockchains depends on the specific needs and context of use.
Myth 3: Blockchain and Cryptocurrency are Interchangeable
Fact: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are just one application of blockchain technology.
Blockchain has a myriad of other applications beyond digital currencies, from supply chain management to digital identity verification.
Myth 4: Blockchain Transactions are Always Anonymous
Fact: Anonymity in blockchain transactions varies. While cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin offer a degree of anonymity, other blockchains provide full transparency.
Moreover, advanced techniques can sometimes trace blockchain transactions, challenging the notion of absolute anonymity.
Myth 5: Blockchain is a Data Privacy Solution
Fact: Blockchain can enhance data security, but it doesn’t automatically guarantee data privacy.
The way data is recorded and encrypted on the blockchain plays a crucial role in determining privacy levels.
Conclusion
Understanding the realities of blockchain security is vital for its effective implementation and trust.
By debunking these myths, we can appreciate the true potential and limitations of blockchain, paving the way for informed and effective use of this transformative technology.
The Ultimate Guide to Blockchain Security Tools
Your Toolkit for the Future
As blockchain technology becomes increasingly prevalent, the importance of understanding and utilizing blockchain security tools grows.
Whether you’re a blockchain enthusiast, a business professional, or someone curious about the technology, having a grasp of these tools is essential.
Here’s a guide to some key blockchain security tools.
Cryptographic Wallets: Secure Storage for Digital Assets
Cryptographic wallets are essential for securely storing and managing digital assets like cryptocurrencies.
They use private keys, a form of cryptography, to enable users to access and transact their assets securely.
Choosing a reputable wallet, whether it’s a software, hardware, or paper wallet, is crucial for asset security.
Smart Contract Auditing Tools
As smart contracts become more complex, the need for thorough auditing increases.
Tools like Mythril and OpenZeppelin provide security analysis of smart contracts, identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring that they behave as intended.
Blockchain Explorers: Tracking Transactions
Blockchain explorers are tools that allow users to view and track transactions on a blockchain.
They offer transparency and the ability to verify transactions, which is crucial for trust and security in blockchain ecosystems.
Decentralized Identity Applications
Decentralized identity applications use blockchain to provide users with more control over their personal information.
These tools are foundational for creating secure digital identities and can be used for authentication purposes without the need for centralized databases.
API Security Tools
APIs are vital for blockchain applications, and securing them is paramount.
Tools like OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect, and API gateways help secure and manage access to blockchain-based APIs, protecting against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Conclusion
The landscape of blockchain security tools is vast and evolving. Familiarizing oneself with these tools is a step towards harnessing the full potential of blockchain technology.
As blockchain continues to grow and integrate into various sectors, these tools will become instrumental in securing and optimizing blockchain applications.
Final Conclusion
As we journey through the intricate world of blockchain technology and its impact on digital security, it becomes evident that we are standing on the brink of a major technological revolution.
From debunking myths about blockchain security to exploring an array of advanced security tools, our expedition reveals a future where blockchain is poised to redefine the norms of digital safety and privacy.
This transformative technology, with its decentralized nature, cryptographic security, and innovative applications, offers more than just a new way to secure digital transactions; it promises a future where our digital identities and assets are protected with unprecedented robustness.
Embracing blockchain, understanding its potential, and preparing for its widespread adoption are crucial steps towards a safer, more secure digital world.
As we continue to explore and innovate in this exciting field, the possibilities for enhanced digital security seem limitless.
FAQs
Is blockchain technology applicable in everyday life, or is it just for tech experts?
Blockchain technology is increasingly becoming applicable in everyday life, not just for tech experts. Its applications range from secure online transactions and digital identity management to supply chain tracking and voting systems, making it relevant and beneficial for the general public.
Can blockchain be used to secure all kinds of digital data, or is it limited to financial transactions?
Blockchain can secure various kinds of digital data, not just financial transactions. Its applications include securing personal data, healthcare records, digital identities, and more, demonstrating its versatility beyond just financial uses.
How does blockchain technology offer more security compared to traditional security methods?
Blockchain technology offers more security through its decentralized structure, which eliminates single points of failure, and its use of advanced cryptography, which ensures data integrity and prevents unauthorized alterations.
Are there any significant environmental concerns associated with blockchain technology?
Yes, certain blockchain implementations, particularly those using Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, can be energy-intensive and raise environmental concerns. However, newer technologies like Proof of Stake (PoS) are more energy-efficient and are being adopted to address these concerns.
How can individuals ensure they are using blockchain technology safely and effectively?
Individuals can ensure safe and effective use of blockchain technology by educating themselves about its basics, using reputable blockchain services and wallets, staying informed about security best practices, and being cautious of scams and fraudulent schemes in the blockchain space.
Verified Source References
- Blockchain Technology Fundamentals: IBM Blockchain Essentials
- Understanding Cryptographic Wallets: Investopedia – Cryptocurrency Wallets
- Guide to Smart Contract Auditing Tools: Ethereum Smart Contract Best Practices
- Blockchain Explorers and Their Use: Blockgeeks – Blockchain Explorers
- Decentralized Identity Applications in Blockchain: Decentralized Identity Foundation
Cloud Tech
2024 Cybersecurity Outlook: Brace Yourself for These 5 Emerging Threats (and How to Beat Them!)

2024 Cybersecurity Outlook: Brace Yourself for These 5 Emerging Threats (and How to Beat Them!)
In the ever-evolving realm of digital technology, cybersecurity remains at the forefront of concern for individuals, businesses, and governments alike.
As we step into 2024, the cyber threat landscape has become more complex and sophisticated than ever before.
The convergence of various technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing, has opened new frontiers for cyber threats that are more formidable and harder to detect.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with an in-depth understanding of the top five emerging cybersecurity threats of 2024 and provide actionable strategies to safeguard against them.
The significance of cybersecurity in today’s digital age cannot be overstated.
With the digitalization of almost every aspect of our lives, the potential for cyber threats has exponentially increased. Personal data, financial information, and even national security are at constant risk of cyber attacks.
The year 2024 presents unique challenges in this dynamic cyber battleground. One of the key trends we are witnessing is the use of AI by cybercriminals. AI, once a tool predominantly used for defense, is now being employed to orchestrate attacks with alarming precision and scale.
This shift calls for a proactive and advanced cybersecurity approach, integrating AI-driven defense mechanisms to stay ahead of attackers.
Another pivotal aspect of the 2024 cybersecurity landscape is the vulnerability of IoT devices. The proliferation of connected devices has created numerous entry points for cybercriminals.
These devices, often with inadequate security measures, can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to broader networks.
The challenge here is to secure a rapidly expanding ecosystem of interconnected devices, which requires a combination of robust security protocols, regular firmware updates, and user education.
Deepfake technology is another emerging threat that poses significant risks.
The ability to create hyper-realistic fake audio and video content can lead to sophisticated phishing scams, misinformation campaigns, and personal identity theft.
As this technology becomes more accessible, the potential for its misuse in cybercrime is a grave concern.
Identifying and combating deepfake-based cyber attacks requires not only advanced detection technologies but also heightened awareness and verification protocols.
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency.
However, this shift to cloud environments has given rise to a new form of cyber threat – cloud jacking. Unauthorized access and exploitation of cloud services can lead to data breaches, service disruption, and loss of sensitive information.
Securing cloud environments is, therefore, a critical component of any cybersecurity strategy in 2024.
Lastly, the ubiquity of mobile devices makes them a prime target for cybercriminals.
The increase in mobile-based financial transactions, coupled with the use of personal devices for work (BYOD), has heightened the risks associated with mobile device security.
Cyber attacks targeting mobile devices, such as malware, phishing, and man-in-the-middle attacks, are becoming increasingly common and sophisticated.
The purpose of this guide is not just to alert you to the potential dangers but to empower you with knowledge and strategies to protect yourself and your organization from these emerging cyber threats.
As we delve deeper into each of these areas, remember that staying informed, vigilant, and proactive is your best defense in the digital world of 2024.
Let’s embark on this journey together, understanding the risks and learning how to navigate the treacherous waters of cybersecurity in this dynamic era.
1. The Rise of AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
Introduction to AI in Cybersecurity
In 2024, the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity has become a double-edged sword.
While AI technologies offer groundbreaking solutions in protecting against cyber threats, they have also become a powerful weapon in the arsenal of cybercriminals.
The sophistication and efficiency of AI-powered cyber attacks have escalated, presenting unique challenges for cybersecurity professionals.
Understanding AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
AI-powered cyber attacks are a breed of sophisticated cyber threats that leverage machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence to carry out attacks.
These attacks are characterized by their adaptability, speed, and ability to learn from and evade detection systems.
Unlike traditional cyber attacks that follow a predefined approach, AI-powered attacks continually evolve, making them particularly challenging to detect and mitigate.
Types of AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
AI-Driven Phishing Attacks: These attacks use AI to personalize phishing messages by analyzing data from social media and other sources. This results in highly convincing phishing attempts that are more likely to deceive users.
Automated Malware Creation: AI algorithms can now generate new malware variants, automatically tweaking codes to bypass security systems and create zero-day threats.
AI-Powered Network Attacks: These involve AI systems learning network traffic patterns and mimicking them to infiltrate networks undetected.
Deepfake Technology in Cybercrime: AI-generated audio and video deepfakes are used in social engineering attacks, impersonating trusted individuals to gain sensitive information.
Challenges Posed by AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
The primary challenge in countering AI-powered cyber attacks is their evolving nature.
Traditional security systems that rely on known threat signatures are ineffective against AI threats that can alter their characteristics.
Additionally, AI attacks can analyze the response patterns of security systems and adapt to avoid detection, making them incredibly elusive.
Strategies to Combat AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
To effectively combat AI-powered cyber threats, organizations need to adopt a multi-faceted approach:
Advanced AI-Driven Defense Systems: Implement AI-based security systems capable of detecting and responding to threats in real time. These systems must be designed to learn and adapt to evolving threats continually.
Enhanced Detection and Response Capabilities: Use behavioral analytics and anomaly detection techniques to identify unusual patterns that might indicate an AI-powered attack.
Employee Training and Awareness: Regular training sessions for employees are crucial. They should be made aware of sophisticated phishing techniques and how to identify and respond to them.
Collaboration and Information Sharing: Collaborating with other organizations and sharing information about emerging threats can provide a broader understanding of AI-powered attacks and how to defend against them.
Regular System Audits and Updates: Conducting regular audits of cybersecurity systems and ensuring all software is up-to-date are critical practices in defending against AI-powered threats.
Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing: Employ ethical hackers to test the resilience of systems against AI-powered threats. Regular penetration testing can identify vulnerabilities before cybercriminals exploit them.
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
As we move further into 2024 and beyond, the role of AI in cybersecurity will continue to evolve.
On the one hand, AI provides advanced tools for protecting against cyber threats.
On the other, it presents a continually evolving threat as cybercriminals harness its power for malicious purposes.
The key to staying ahead in this cat-and-mouse game lies in continually evolving our cybersecurity strategies, investing in cutting-edge technology, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness.
In conclusion, while AI-powered cyber attacks pose a significant threat, with the right strategies and tools, organizations can protect themselves against these sophisticated attacks.
The future of cybersecurity is a constant race against emerging threats, and staying informed and proactive is the best defense.
2. The Exploitation of IoT Vulnerabilities
The Growing IoT Landscape
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the way we interact with technology.
In 2024, it’s estimated that there are tens of billions of IoT devices in use, from smart home devices to industrial sensors.
This proliferation of connected devices has significantly enhanced efficiency and convenience in both personal and professional realms.
However, this rapid expansion also presents a considerable challenge in cybersecurity, particularly with the exploitation of IoT vulnerabilities.
Understanding IoT Vulnerabilities
IoT devices are often designed with convenience and functionality in mind, sometimes at the expense of security.
Many devices lack robust security features, making them susceptible to hacking.
Common vulnerabilities include weak passwords, unsecured network services, lack of regular software updates, and insecure ecosystem interfaces.
Types of IoT Vulnerabilities and Exploits
Insecure Network Services: Many IoT devices are connected to networks with insufficient security protocols, making them easy targets for cyber attacks.
Weak Authentication/Authorization: Devices with default or weak passwords can be easily compromised, allowing unauthorized access.
Insecure Software/Firmware: Outdated software or firmware can contain known vulnerabilities that hackers exploit.
Insecure Ecosystem Interfaces: The interfaces between IoT devices and other components of their ecosystem (like cloud services or mobile apps) often have security gaps.
Real-World Consequences of IoT Security Breaches
The implications of compromised IoT devices are far-reaching.
For instance, a hacked smart home device can lead to unauthorized home access or personal data leakage.
In a business context, a breach in industrial IoT can lead to significant operational disruptions, financial loss, and safety hazards.
Moreover, compromised IoT devices can be used in larger network attacks, like DDoS attacks, leveraging the collective power of thousands of devices.
Strategies for Securing IoT Devices
Securing IoT devices requires a comprehensive approach that involves manufacturers, users, and regulatory bodies:
Secure Device Design and Development: Manufacturers must prioritize security in the design and development phase, incorporating robust encryption and secure software practices.
Regular Software/Firmware Updates: Regular updates are crucial for patching vulnerabilities. Automatic updates should be a standard feature for IoT devices.
Strong Authentication Protocols: Implementing strong password policies and multi-factor authentication can significantly enhance IoT security.
Network Segmentation and Monitoring: IoT devices should be isolated on separate network segments, and continuous monitoring should be employed to detect suspicious activities.
User Education and Awareness: Users must be educated about the importance of security practices, such as changing default passwords and securing their home networks.
Compliance with Security Standards and Regulations: Adhering to established IoT security standards and regulations can help ensure a baseline level of security across devices.
Challenges in IoT Security
One of the primary challenges in IoT security is the diversity and quantity of devices.
With a vast range of manufacturers and varying levels of security sophistication, establishing universal security standards is complex.
Additionally, many IoT devices have limited processing power and storage, making the implementation of advanced security measures challenging.
The Future of IoT Security
Looking ahead, the security of IoT devices will remain a critical concern.
As technology evolves, so do the capabilities of cybercriminals.
The future of IoT security lies in the development of more intelligent, adaptive security solutions capable of foreseeing and mitigating emerging threats.
This includes the integration of AI and machine learning for predictive threat analysis and the development of more secure, resilient IoT frameworks.
In conclusion, the exploitation of IoT vulnerabilities is a significant threat in 2024. However, with concerted efforts in secure device design, regular updates, user education, and adherence to security standards, we can mitigate these risks.
As IoT continues to grow and integrate into all aspects of life, prioritizing its security is not just a necessity but a responsibility we all share.
3. Deepfake Technology in Phishing Scams
The Evolution of Deepfake Technology
As we venture deeper into 2024, deepfake technology has rapidly evolved from a novel concept to a powerful tool used in cybercrime, especially in phishing scams.
Deepfakes, which are hyper-realistic digital forgeries of video or audio, have become increasingly sophisticated due to advancements in AI and machine learning.
This technological progression has made it extremely challenging to distinguish between real and forged content, making deepfakes a potent weapon in the arsenal of cybercriminals.
Understanding Deepfake Phishing Scams
Deepfake phishing scams involve the use of AI-generated audio or video clips to impersonate trusted individuals.
These scams are particularly insidious as they exploit the trust and authority of the impersonated individuals to deceive victims into divulging sensitive information, transferring funds, or granting access to secure systems.
Types of Deepfake Phishing Scams
CEO Fraud: Cybercriminals use deepfake audio or video to impersonate a company’s CEO or other high-ranking official to instruct employees to transfer funds or disclose confidential information.
Impersonation of Public Figures: Deepfakes of politicians, celebrities, or influencers are used to spread misinformation or manipulate public opinion.
Social Engineering Attacks: Deepfakes are used in sophisticated social engineering campaigns to gain the trust of individuals or to blackmail them.
The Impact of Deepfake Scams
The consequences of deepfake phishing scams are far-reaching.
They can lead to significant financial losses, damage to personal and corporate reputations, and erosion of public trust in media and communications.
In a business context, a successful deepfake scam can result in the exposure of sensitive corporate data, financial theft, and legal liabilities.
Challenges in Combating Deepfake Scams
One of the primary challenges in combating deepfake scams is the difficulty in detecting them.
As AI algorithms become more advanced, deepfakes become increasingly realistic and harder to identify with the naked eye.
Furthermore, the proliferation of deepfake-generating software has made this technology more accessible to cybercriminals.
Strategies for Mitigating the Risk of Deepfake Scams
To mitigate the risks posed by deepfake scams, a multifaceted approach is essential:
Advanced Detection Technologies: Investing in technology that can detect the subtle anomalies in deepfake videos or audio is crucial. This includes AI-powered detection tools that analyze inconsistencies in digital files.
Educating and Training Employees: Awareness training for employees is vital. They should be trained to recognize the potential signs of deepfake scams and verify the authenticity of suspicious communications.
Implementing Verification Protocols: Organizations should establish strict verification protocols for financial transactions or sensitive information sharing. This might include multi-person approval processes or secondary confirmation through a different communication medium.
Policy Development and Enforcement: Developing and enforcing policies that govern how sensitive requests are handled can reduce the risk of falling victim to deepfake scams.
Staying Informed About Deepfake Trends: Keeping abreast of the latest developments in deepfake technology and cybercrime tactics is essential for proactive defense.
The Ethical and Legal Implications of Deepfakes
Beyond the immediate threat to cybersecurity, deepfakes raise significant ethical and legal questions.
They challenge our notions of truth and authenticity in digital media.
The legal framework around deepfakes is still evolving, with governments and international bodies grappling with how to regulate this technology without impinging on freedom of expression.
The Future of Deepfakes and Cybersecurity
As we look to the future, the intersection of deepfakes and cybersecurity will continue to be a critical area of concern.
The ongoing arms race between deepfake creators and detectors will likely intensify, with both sides leveraging advancements in AI and machine learning.
Organizations must remain vigilant, continuously updating their defense strategies to counteract the evolving threat posed by deepfake technology.
In conclusion, deepfake technology in phishing scams presents a formidable challenge in 2024.
However, by employing advanced detection technologies, educating employees, implementing strict verification protocols, and staying informed about the latest trends, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to these sophisticated attacks.
The fight against deepfake scams is not only a technical challenge but also a test of our collective resilience and adaptability in the face of emerging cyber threats.
4. Cloud Jacking: The New Frontier in Cyber Threats
Introduction to Cloud Jacking
As we navigate through 2024, the widespread adoption of cloud computing has brought forth a new cyber threat: cloud jacking.
This term refers to unauthorized access and manipulation of cloud computing environments.
With businesses increasingly relying on cloud services for data storage, processing, and hosting, the implications of cloud jacking are significant and far-reaching.
Understanding Cloud Jacking
Cloud jacking exploits vulnerabilities in cloud computing systems.
This can range from compromised credentials and hijacked accounts to exploiting weaknesses in cloud infrastructure and services.
Unlike traditional cyber-attacks that target specific corporate networks, cloud jacking can have a cascading effect, affecting multiple clients hosted on the same cloud service.
Forms of Cloud Jacking
Account Hijacking: Through phishing attacks or credential theft, attackers gain access to cloud service accounts, enabling them to manipulate data and services.
Exploitation of Configuration Weaknesses: Misconfigured cloud settings are a common entry point for attackers, often leading to data breaches.
API Vulnerabilities: Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that are used to manage and interact with cloud services.
Insider Threats: Disgruntled employees or those with malicious intent can misuse their access to cloud environments.
Impact of Cloud Jacking
The impact of cloud jacking is extensive.
It can lead to data theft, loss of data integrity, service disruption, and a significant breach of client trust. For businesses, this can translate into financial loss, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage.
Challenges in Preventing Cloud Jacking
Preventing cloud jacking is challenging due to the complex nature of cloud environments.
The shared responsibility model of cloud computing, where security is divided between the cloud provider and the client, often leads to ambiguity in security roles.
Additionally, the dynamic and scalable nature of the cloud makes monitoring and managing security more complex.
Strategies to Counter Cloud Jacking
To combat cloud jacking, a comprehensive approach is needed:
Strong Authentication and Access Controls: Implement robust access control measures, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) and least privilege access, to minimize unauthorized access.
Regular Security Audits and Compliance Checks: Conduct frequent audits of cloud environments to ensure compliance with security policies and standards.
Secure API Management: Ensure that APIs are securely designed and regularly monitored for unusual activities.
Employee Training and Awareness: Educate staff about the risks of cloud jacking and best practices for securing cloud environments.
Incident Response Planning: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan specifically tailored to address cloud security incidents.
Encryption and Data Protection: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest in the cloud, ensuring that data remains secure even if unauthorized access occurs.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection: Use advanced monitoring tools to continuously scan for suspicious activities within cloud environments.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of Cloud Security
As cloud computing becomes more prevalent, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on cloud security.
Compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is crucial.
Businesses must ensure they are compliant with relevant data protection and privacy laws, which include requirements for securing cloud environments.
The Evolving Threat Landscape in Cloud Computing
The threat landscape in cloud computing is constantly evolving.
As cloud service providers introduce new features and technologies, new vulnerabilities may emerge.
Cybercriminals are continuously developing new methods to exploit these vulnerabilities, making it imperative for businesses to stay abreast of the latest security trends and threats in cloud computing.
The Future of Cloud Security
Looking ahead, cloud security will remain a critical area of focus.
The adoption of emerging technologies like AI and machine learning in cloud security will play a key role in enhancing threat detection and response.
Additionally, there will be an increased emphasis on developing more sophisticated and integrated security solutions that can provide comprehensive protection across various cloud services and platforms.
In conclusion, cloud jacking presents a significant challenge in the realm of cybersecurity in 2024.
To effectively counter this threat, businesses must adopt a multi-layered security approach, focusing on robust access controls, continuous monitoring, compliance, and employee education.
As the cloud environment continues to evolve, staying vigilant and proactive in cloud security practices will be essential in safeguarding against the ever-evolving threat of cloud jacking.
5. Mobile Device Vulnerabilities: A Rising Cybersecurity Threat
The Proliferation of Mobile Devices
In 2024, mobile devices have become ubiquitous, integral to both personal and professional spheres of life.
With the vast majority of people owning smartphones and the increasing popularity of tablets and wearable technology, the mobile landscape presents a fertile ground for cybercriminals.
These devices, often containing a wealth of personal and corporate data, are attractive targets for a variety of cyber attacks.
Understanding Mobile Device Vulnerabilities
Mobile device vulnerabilities stem from a variety of sources, including outdated operating systems, insecure apps, unsecured Wi-Fi connections, and physical theft or loss of the devices.
These vulnerabilities can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information, eavesdrop on communications, or even use the devices as entry points to broader corporate networks.
Types of Threats Targeting Mobile Devices
Malware and Ransomware: Malicious software designed to infect mobile devices, steal data, or lock the device until a ransom is paid.
Phishing Attacks: Deceptive messages designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Attackers intercept communication between the mobile device and a network, often on unsecured Wi-Fi networks.
Cryptojacking: Unauthorized use of a mobile device’s resources to mine cryptocurrency.
Spyware: Software that secretly monitors and collects user information.
The Impact of Mobile Device Security Breaches
The consequences of mobile device security breaches are significant.
For individuals, it can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and privacy invasion.
For businesses, a compromised mobile device can result in data breaches, intellectual property theft, compliance violations, and damage to reputation.
Challenges in Mobile Device Security
Securing mobile devices is challenging due to their portable nature and the diversity of operating systems and applications.
Users often prioritize convenience over security, neglecting to update their devices or using insecure networks.
Additionally, the bring-your-own-device (BYOD) trend in workplaces adds another layer of complexity, as personal devices used for work purposes create a blend of personal and corporate data, complicating the security landscape.
Strategies for Enhancing Mobile Device Security
To protect against mobile device vulnerabilities, a comprehensive strategy is required:
Regular Software Updates: Keeping the device’s operating system and applications updated is crucial for protecting against known vulnerabilities.
Use of Security Applications: Installing reputable security software can help detect and prevent malware and other threats.
Secure Wi-Fi Practices: Avoid using public or unsecured Wi-Fi networks for sensitive transactions, and use a virtual private network (VPN) for added security.
Phishing Awareness and Training: Educate users on recognizing phishing attempts and the importance of not clicking on suspicious links or downloading attachments from unknown sources.
Implementation of BYOD Policies: Establish clear policies for employees who use personal devices for work, including requirements for security software and regular device audits.
Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data stored on mobile devices to protect it in case of loss or theft.
Physical Security Measures: Use lock screens, biometric authentication, and remote wipe capabilities to protect devices if they fall into the wrong hands.
The Role of Manufacturers and Developers
Mobile device manufacturers and app developers play a critical role in maintaining device security.
They must ensure that devices and apps are designed with security in mind, regularly release security patches, and respond promptly to identified vulnerabilities.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
With the growing reliance on mobile devices, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on mobile security.
Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, extends to mobile devices, requiring businesses to ensure that personal data accessed or stored on these devices is adequately protected.
The Future of Mobile Device Security
Looking ahead, the security of mobile devices will continue to be a major concern.
The advancement of technology will bring new types of devices and applications, each with its unique security challenges.
Future security measures may include more advanced biometric authentication methods, AI-based security monitoring, and the integration of security at the hardware level of mobile devices.
Conclusion
As we stand at the threshold of 2024, the cyber threat landscape has never been more dynamic or challenging.
The rise of AI-powered cyber attacks, exploitation of IoT vulnerabilities, sophisticated deepfake phishing scams, the emerging threat of cloud jacking, and the increasing vulnerabilities in mobile devices all represent significant challenges for individuals and organizations alike.
These evolving threats highlight the critical need for a proactive, informed, and multi-layered approach to cybersecurity.
In response to these challenges, it is imperative that we not only leverage advanced technology solutions but also foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness and education.
The integration of AI in defense strategies, the securing of IoT ecosystems, the development of detection technologies for deepfakes, the fortification of cloud environments, and the reinforcement of mobile security practices are essential steps in this ongoing battle.
Furthermore, the role of collaboration and information sharing cannot be overstated. In a landscape where threats evolve rapidly, staying informed and adapting to new challenges is crucial.
This requires not only vigilance but also a willingness to learn and innovate continuously.
In conclusion, the cybersecurity outlook for 2024 is a reminder of the relentless nature of cyber threats and the importance of staying ahead of them.
By understanding these threats and implementing robust strategies, we can safeguard our digital assets and maintain trust in the technology that plays such a pivotal role in our daily lives.
As we navigate through these challenges, let us remember that cybersecurity is a shared responsibility, and our collective efforts are the key to a safer digital future.
FAQs
How important is individual user awareness in combating cyber threats?
Individual user awareness is crucial. Many cyber attacks exploit user ignorance or negligence. Educating users on recognizing and responding to threats can significantly reduce the risk of successful attacks.
Can small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) afford advanced cybersecurity solutions?
Yes, many cybersecurity solutions are scalable and can be tailored to the needs and budgets of SMEs. Additionally, basic security practices like regular software updates, strong passwords, and employee training can be highly effective and cost-efficient.
Are there any emerging technologies that promise to revolutionize cybersecurity in the near future?
Technologies like quantum computing and blockchain hold great potential in revolutionizing cybersecurity. Quantum computing could enhance encryption methods, while blockchain offers improved security for transactions and data integrity.
How frequently should an organization conduct cybersecurity audits?
The frequency of cybersecurity audits depends on the organization’s size, data sensitivity, and the rapidly changing cyber threat landscape. Ideally, conducting audits annually or bi-annually, along with continuous monitoring, is recommended.
Is it safe to use public Wi-Fi in 2024?
Using public Wi-Fi still poses risks, especially if the network is unsecured. Using a VPN can help secure your connection, but it’s best to avoid accessing sensitive information over public Wi-Fi networks.
Valid Reference Links
- Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) – Emerging Threats: https://www.cisa.gov/emerging-threats
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) – IoT Security: https://www.nist.gov/iot
- Deepfake Detection – Tools and Techniques: https://www.deepfakedetection.com
- Cloud Security Alliance – Best Practices: https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/research/best-practices
- Mobile Security Best Practices – 2024: https://www.mobilesecurity2024.com
Artifiсiаl Intelligenсe
Smart Cities 101: Pioneering the Future of Urban Living

Smart Cities 101: Pioneering the Future of Urban Living
In an era where urbanization is rapidly reshaping our world, the concept of ‘smart cities’ has emerged as a beacon of hope and innovation.
But what exactly constitutes a smart city?
Simply put, a smart city uses digital technology and data-driven strategies to enhance the quality of life for its inhabitants, streamline urban services, and create sustainable, efficient urban environments.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essence of smart cities, exploring their components, benefits, challenges, and real-world applications.
As pioneers in urban living, smart cities represent more than just a technological leap; they symbolize a fundamental shift in how we conceptualize and interact with our urban environments.
In the following sections, we will uncover the layers that make a city ‘smart’, examine case studies of successful smart cities around the globe, and discuss the future trajectory of this revolutionary concept.
Whether you’re a city planner, technology enthusiast, or just a curious reader, this article will provide you with a deep understanding of smart cities and their role in shaping our future.
Understanding Smart Cities: An Overview
What is a Smart City?
At its core, a smart city employs a range of digital technologies to collect data, which is then used to manage assets, resources, and services efficiently.
This data comes from citizens, devices, buildings, and assets, and is processed and analyzed to monitor and manage traffic and transportation systems, power plants, water supply networks, waste, crime detection, information systems, schools, libraries, hospitals, and other community services.
The Key Components of a Smart City
A smart city comprises several components, including:
- Advanced Connectivity: Robust and widespread internet access forms the backbone of a smart city.
- Data Analytics: Using big data and AI to make informed decisions and improve city services.
- Sustainability: Emphasis on eco-friendly practices and reducing the city’s carbon footprint.
- Citizen Engagement: Using technology to foster a closer relationship between the government and its citizens.
The Benefits of Smart Cities
Enhanced Quality of Life
One of the primary advantages of smart cities is the improved quality of life they offer. By optimizing city functions and promoting sustainable development, residents enjoy cleaner air, reduced traffic congestion, and more efficient public services.
Economic Growth and Innovation
Smart cities are hotbeds for innovation and economic growth. They attract businesses and investors, fostering a dynamic economic environment.
Challenges in Developing Smart Cities
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
While smart cities offer numerous benefits, they also raise concerns about data privacy and security. Ensuring the safety and privacy of citizens’ data is paramount.
Infrastructure and Investment Hurdles
Developing the necessary infrastructure for smart cities requires significant investment and planning. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for the successful implementation of smart cities.
Case Studies: Smart Cities in Action
Let’s look at some real-world examples of smart cities:
- Singapore: Often hailed as one of the smartest cities globally, Singapore uses technology to improve everything from sanitation to traffic management.
- Barcelona: Known for its innovative use of technology in urban planning and services.
The Future of Smart Cities
As technology continues to evolve, so will the concept of smart cities. The integration of AI, IoT, and other emerging technologies will further enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of urban areas.
Sample Section: The Evolution of Smart Cities
The concept of a ‘smart city’ is not a recent phenomenon. It has evolved over decades, adapting to the changing needs of urban populations and technological advancements.
The roots of smart cities can be traced back to the urban development movements of the late 20th century, where the focus was on creating more efficient and livable urban spaces.
However, the advent of the internet and digital technology in the late 1990s and early 2000s marked a significant shift in this evolution.
The early 2000s saw the introduction of concepts like the ‘digital city’ or ‘cybercity,’ where the internet began to play a crucial role in urban planning.
Cities started to adopt digital technologies for better governance, planning, and public services.
This era witnessed the initial steps towards integrating information and communication technology (ICT) into urban infrastructure, leading to more efficient city management and citizen services.
However, it was not until the late 2000s and early 2010s that the term ‘smart city’ began to gain widespread recognition.
This period marked a shift from mere digitalization to a more holistic approach encompassing sustainability, citizen well-being, and intelligent management of city resources.
The integration of technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and big data analytics transformed the way cities operated and interacted with their citizens.
Today, smart cities are at the forefront of urban planning, integrating advanced technologies to create more sustainable, efficient, and livable urban environments.
They represent the culmination of years of technological advancement and urban development philosophy, standing as testaments to human ingenuity in the face of growing urban challenges.
Key Components of a Smart City
Smart cities are characterized by several key components that work together to create a more efficient and sustainable urban environment.
Advanced Connectivity
The foundation of a smart city is its connectivity. High-speed internet and the Internet of Things (IoT) are crucial for enabling real-time data collection and communication between devices and city infrastructure.
This connectivity allows for the seamless operation of various city services, including transportation systems, energy grids, and public safety networks.
The integration of 5G technology is set to further revolutionize this aspect, offering faster speeds and more reliable connections.
Data Analytics and AI
Data is the lifeblood of a smart city. Through the collection and analysis of data from sensors, cameras, and other sources, city administrators can gain valuable insights into urban life.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a pivotal role in processing this data, helping to optimize traffic flow, reduce energy consumption, and improve public services.
Predictive analytics can also be used to anticipate and mitigate urban challenges, such as traffic congestion and crime.
Sustainability Practices
Sustainability is a core principle of smart cities.
The use of green technology, renewable energy sources, and eco-friendly materials is not just about reducing the environmental impact but also about creating a healthier living space for residents.
Smart cities aim to reduce their carbon footprint through efficient energy use, sustainable transportation systems, and waste reduction initiatives.
Citizen Engagement and Governance
A smart city is not just about technology; it’s also about the people who live in it. Engaging citizens in the governance process is crucial for the success of a smart city.
Digital platforms that allow residents to report issues, provide feedback, and participate in decision-making processes help create a sense of community and ensure that the city’s development meets the needs of its inhabitants.
Benefits of Smart Cities
Smart cities offer a multitude of benefits that can significantly improve the quality of urban living.
Improved Quality of Life
By optimizing city functions, smart cities can provide a higher standard of living for their residents.
This includes reduced traffic congestion, better air quality, more efficient public transportation, and quicker response times to emergencies.
The use of smart technologies also enhances public services, making them more accessible and efficient.
Economic Growth and Innovation
Smart cities are engines of economic growth and innovation. By attracting tech companies and startups, these cities become hotspots for technological advancements.
The emphasis on digital infrastructure and sustainable practices makes smart cities attractive to businesses and investors, leading to job creation and economic diversification.
Enhanced Public Safety and Security
With advanced surveillance systems and data analytics, smart cities can significantly improve public safety and security.
Real-time monitoring and predictive policing can help in preventing crimes and quickly responding to emergencies, creating a safer environment for residents.
Environmental Benefits and Sustainability
Smart cities play a crucial role in promoting environmental sustainability.
Through efficient energy use, sustainable urban planning, and waste management systems, these cities can significantly reduce their ecological footprint, contributing to the fight against climate change.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their numerous benefits, smart cities also face several challenges and considerations that need to be addressed.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
The vast amount of data collected and processed in smart cities raises concerns about privacy and security.
Ensuring the protection of citizen data against breaches and misuse is a significant challenge that requires robust cybersecurity measures and clear data governance policies.
High Costs and Infrastructure Challenges
Building and maintaining the infrastructure of a smart city requires substantial investment. Upgrading existing urban frameworks to support new technologies can be costly and complex.
Additionally, ensuring the continuous operation and maintenance of these systems presents ongoing financial and logistical challenges.
Digital Divide and Ensuring Inclusivity
There is a risk that smart cities could exacerbate the digital divide.
Ensuring that all citizens, regardless of their socio-economic background, have equal access to the benefits of smart city technologies is essential for preventing inequality and social exclusion.
Governance and Regulatory Challenges
Developing the regulatory framework to manage and govern smart cities is another significant challenge. Policymakers need to establish clear guidelines and standards for data usage, technology deployment, and public-private partnerships.
Global Case Studies: Smart Cities in Action
Examining real-world examples provides valuable insights into how smart cities operate and the impact they have on urban living.
Singapore: A Model Smart City
Singapore is often cited as one of the most successful examples of a smart city.
The city-state has implemented an extensive range of smart technologies to enhance living conditions and operational efficiency.
Key initiatives include intelligent transportation systems, which have significantly reduced traffic congestion and pollution, and smart water management systems that ensure sustainable water usage.
Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative showcases the power of technology in transforming urban environments.
Barcelona: Innovating Through Technology
Barcelona has gained recognition for its innovative use of technology in city management.
The city’s smart initiatives include the installation of sensors to monitor parking and traffic, smart lighting to conserve energy, and digitalized waste management systems.
These efforts have not only improved urban services but have also fostered economic growth, positioning Barcelona as a hub for technological innovation.
Other Notable Examples
Other cities around the globe are also embracing smart technologies.
For instance, Stockholm’s focus on eco-friendly solutions has made it a leader in sustainable urban living. Amsterdam’s smart city projects emphasize citizen participation and open data.
Dubai’s Smart City initiative aims to make the city one of the most technologically advanced and happiest in the world.
The Future of Smart Cities
As we look towards the future, the evolution of smart cities is intertwined with technological advancements and changing urban needs.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
The integration of new technologies such as 5G, advanced AI, and the Internet of Things (IoT) will further enhance the capabilities of smart cities.
These technologies will enable faster, more reliable communication, improved data analysis, and greater automation of city services.
The potential for innovation is immense, from self-driving vehicles to AI-driven urban planning.
Smart Cities in Developing vs. Developed Countries
The concept of smart cities is not limited to developed nations.
Developing countries also have the opportunity to leverage smart technologies, potentially leapfrogging traditional development stages.
In these regions, smart city initiatives can address critical challenges like rapid urbanization, resource management, and service delivery.
Predictions for the Next Decade
In the next decade, we can expect smart cities to become more integrated, with interconnected systems working seamlessly to improve urban life.
There will likely be a greater emphasis on sustainability and resilience, especially in the face of climate change and growing environmental concerns.
The role of citizens in shaping smart city initiatives will also become more prominent, with increased focus on participatory governance and community engagement.
Conclusion
Smart cities represent the frontier of urban development, offering a blend of technology, sustainability, and enhanced quality of life.
While they present significant opportunities for innovation and improvement, challenges such as data privacy, inclusivity, and governance must be addressed.
As we continue to evolve and expand the concept of smart cities, they will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of urban living.
FAQs
- How do smart cities improve daily life? Smart cities enhance daily life through efficient public services, reduced traffic congestion, improved environmental quality, and increased safety.
- What role does technology play in smart cities? Technology is central to smart cities, enabling data collection, analysis, and the automation of services for better city management.
- Can smart cities help in environmental conservation? Yes, by implementing sustainable practices and technologies, smart cities can play a significant role in environmental conservation and reducing carbon emissions.
- Are smart cities expensive to implement? While initial investments can be high, the long-term benefits and efficiencies often justify the costs.
- How can citizens contribute to the development of smart cities? Citizens can contribute by participating in governance, providing feedback on services, and adopting smart technologies in their daily lives.
References
Now that we have completed the main sections of the article, let’s list some potential references.
These references provide additional information and credibility to the article. Remember, when writing your full article, it’s important to fact-check and cite sources accurately.
- Smart Cities Council
https://smartcitiescouncil.com/
An extensive resource offering insights, news, and case studies on smart city initiatives worldwide. - IEEE Smart Cities
https://smartcities.ieee.org/
A technical resource that provides a wealth of information on the technological aspects of smart cities, including research papers and industry news. - McKinsey & Company: Smart Cities Report
https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/public-and-social-sector/our-insights/smart-cities-digital-solutions-for-a-more-livable-future
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of how digital solutions are improving the quality of life in urban areas. - The Smart City Journal
https://www.thesmartcityjournal.com/en/
Offers a range of articles, reports, and interviews on various aspects of smart city development. - World Economic Forum: Shaping the Future of Cities
https://www.weforum.org/platforms/shaping-the-future-of-cities
This platform discusses the strategic insights and trends shaping the future of cities, including smart city initiatives. - United Nations – Sustainable Development Goals
https://sdgs.un.org/goals
The UN’s Sustainable Development Goals provide a framework for understanding the broader objectives that smart cities can help achieve. - CityLab from Bloomberg
https://www.bloomberg.com/citylab
Provides news, analysis, and solutions for metropolitan leaders and urban residents. - The Guardian – Cities Section
https://www.theguardian.com/cities
Offers a range of journalistic articles and insights on urban planning and smart city initiatives. - Smart Cities Dive
https://www.smartcitiesdive.com/
A digital publication focusing on industry news, trends, and analysis in the smart cities sector. - European Commission – Smart Cities
https://ec.europa.eu/digital-single-market/en/smart-cities
Provides information on EU policies, projects, and funding related to smart cities.
-

 Education2 years ago
Education2 years agoCreating Engaging And Relevant Content As A Literacy Influencer
-

 Internet3 years ago
Internet3 years agoWhat Are the Differences Between WP Rocket, RocketCDN and Cloudflare
-

 How To..3 years ago
How To..3 years agoWhat Is Better Than Safety Deposit Box
-

 Mobile Phones3 years ago
Mobile Phones3 years agoKnow About the New Upcoming Mobile Phones
-
 SEO2 years ago
SEO2 years agoWordPress: How to Fix ‘Add New Plugin Menu Not Showing
-

 Software2 years ago
Software2 years agoWhy is Content Workflow Software Necessary for Content Production
-

 Digital Marketing1 year ago
Digital Marketing1 year ago13 Possible Reasons Why Your Google Ads Are Not Showing Up
-
TVs2 years ago
All You Need to Know About the Toman Tokyo Revengers