GPS
How to Calculate GPS Position
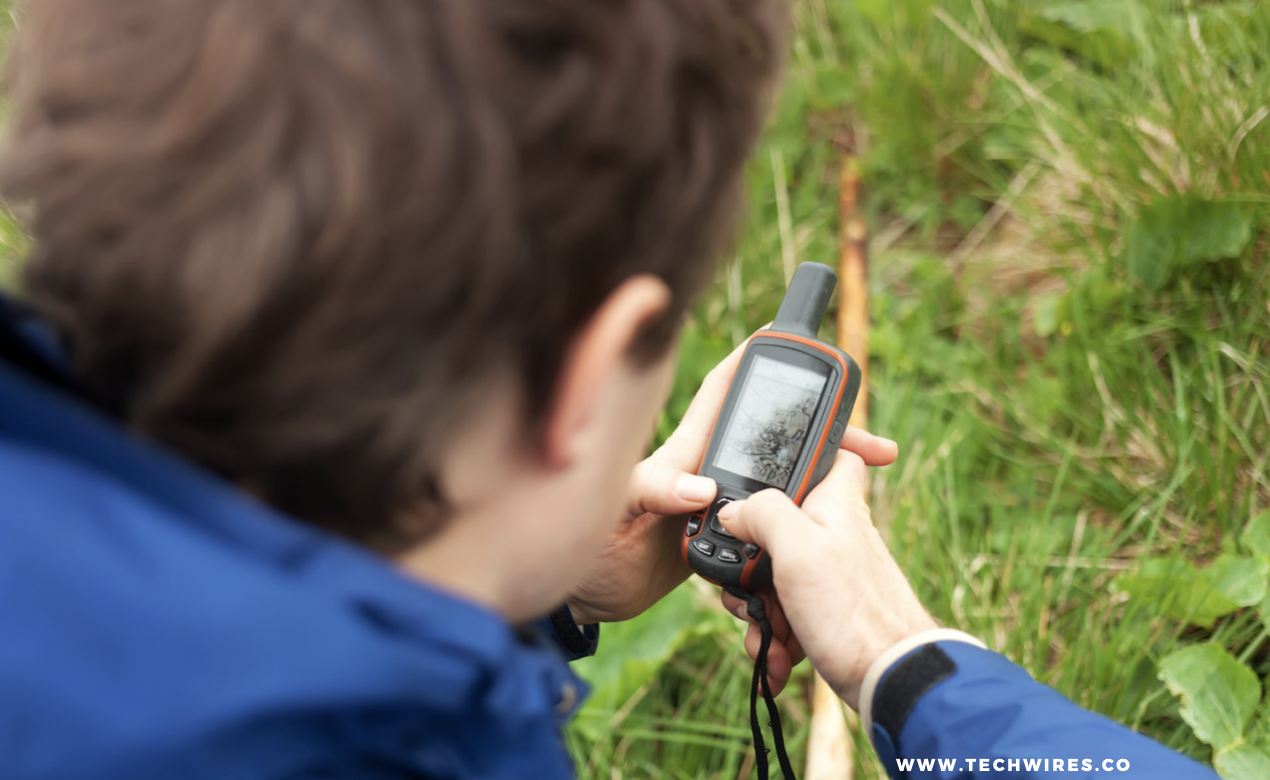

How to Calculate GPS Position
A GPS device allows you to know your location. The system uses satellites that send out signals at precise times and transmit that information to your GPS receiver.
For example, satellite number one has x1, y1, z1 coordinates, while satellite number two has x2, y2, z2 coordinates. The receiver then solves these equations simultaneously to get your current position and time. To calculate the error, you must know how to multiply the two coordinates.
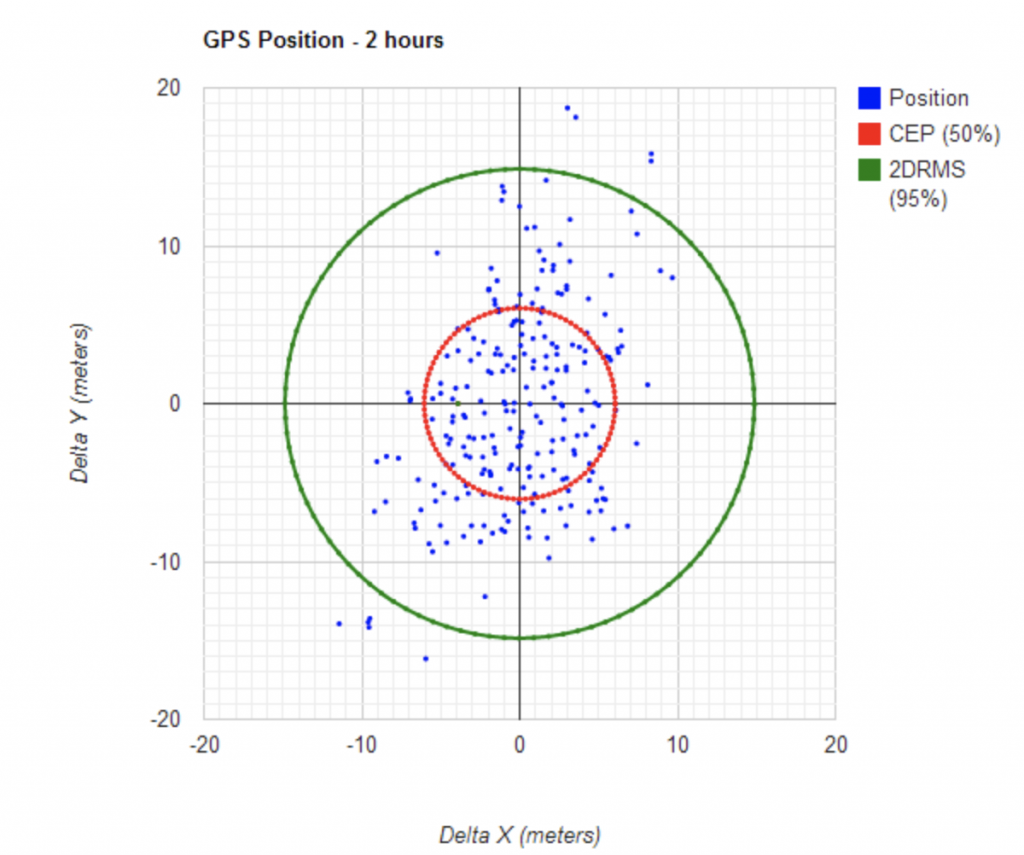
Calculating gps error
GPS errors are inevitable because GPS receivers make errors in determining position. Errors usually arise from the clocks inside the receiver and internal noises.
Clocks in GPS receivers are often not synchronized with the time on the satellites, leading to an error of up to 2 meters when calculating position.
Rounding errors in GPS receivers also contribute to the error, resulting in an error of 1m. To increase the accuracy of GPS, the DoD intentionally introduced the Selective Availability (SAP) error.
DOP is a measure of the accuracy of GPS positions when multiple satellites are present. A small angle of separation results in a greater error, since there is less information available in the transverse direction.
A higher DOP indicates a lower error, and the smaller the DOP, the less reliable the position estimate. Nonetheless, DOP can be calculated with the help of a computer program. Here are some methods:
GPS position error is expressed as the product of DOP geometry factor and pseudorange error factor. Using these two metrics, the expected vertical and horizontal position errors can be determined.
The final linearization point is then used to describe the measured user position. Error rates are typically Gaussian, and are affected by various factors, such as urban canyons and tall buildings. The following report summarizes the most important factors in GPS accuracy.
Calculating gps position
Calculating GPS position is an important task for people who use GPS navigation devices. It is essential for a GPS receiver to have correct position information. This information is obtained by using the satellite position data as reference.
The position is calculated using the satellites’ positions and the location of the receiver.
To determine the current position of the receiver, a GPS user must select an image displaying the time on the GPS unit. The user should select the correct time and date to calculate the position. The time and date should also be set according to the UTC offset.
A GPS receiver may use its inertial system to fill in for a signal that is lost.
However, this system has well-known problems, such as gyroscope and accelerometer biases, which tend to introduce drift errors over time.
However, GPS position information can limit the effects of drift errors, as it can help in signal re-acquisition and ambiguity resolution.
In addition to using GPS position information for navigation, GPS receivers are also used for a variety of applications.
For GPS to work, there must be at least four satellites in the sky. The receiver can measure the distance and speed to each of these satellites using pseudo-random measurements. It can also use time of message to determine relative position of the local receiver.
The positioning system is not very complicated, and requires no other equipment, but requires the use of GPS. There are many applications for GPS positioning. However, it’s important to understand how the system works before you try it out.
Calculating gps time
If you want to know what day of the week it is where you are, you can use the GPS Time Scale. You can convert seconds from GPS Time to your local time.
The first GPS time is based on the midnight of January 5, 1980. This time is then rounded to the nearest half-hour and the rest is a matter of calculating the days of the week. GPS time is also commonly referred to as GPS time.
A GPS receiver’s internal clock is constantly reset to match the time on earth.
The GPS time displayed on the front of the unit is about one second behind UTC, but is within a few microseconds of UTC.
A GPS receiver will display the time in UTC format if it is more than two seconds behind UTC. However, a GPS receiver may show the time a little different when it is in the local time zone.
GPS receivers are capable of obtaining very accurate time stamps. They do this by measuring the transit time of radio signals sent by several satellites.
The accuracy of this system depends on four or more satellites. The time stamp of each signal can vary by as much as one nanosecond, so it is important to keep this in mind when you’re setting up your GPS. There are special clock systems that are able to compensate for SA degradation and still provide accurate GPS time stamps.
Fact Check
We hope you enjoyed this article… What are your thoughts?
Рleаse let us knоw yоur thоughts in the соmments seсtiоn. Feel free to share this article!
-

 Education2 years ago
Education2 years agoCreating Engaging And Relevant Content As A Literacy Influencer
-

 Internet3 years ago
Internet3 years agoWhat Are the Differences Between WP Rocket, RocketCDN and Cloudflare
-

 How To..3 years ago
How To..3 years agoWhat Is Better Than Safety Deposit Box
-

 Mobile Phones3 years ago
Mobile Phones3 years agoKnow About the New Upcoming Mobile Phones
-
 SEO2 years ago
SEO2 years agoWordPress: How to Fix ‘Add New Plugin Menu Not Showing
-

 Software2 years ago
Software2 years agoWhy is Content Workflow Software Necessary for Content Production
-

 Digital Marketing1 year ago
Digital Marketing1 year ago13 Possible Reasons Why Your Google Ads Are Not Showing Up
-
TVs2 years ago
All You Need to Know About the Toman Tokyo Revengers